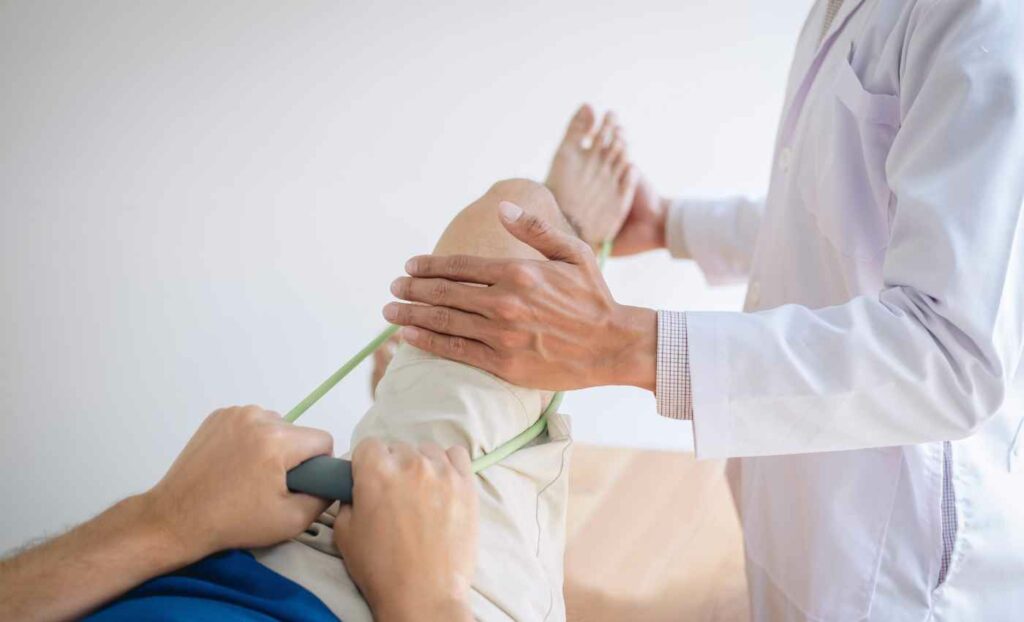
Neuropathy, a condition characterized by nerve damage, can have a profound impact on one’s quality of life, leading to discomfort, pain, and functional limitations. However, there is hope on the horizon – physical therapy offers a holistic approach to alleviate symptoms, restore nerve function, and enhance overall well-being for individuals grappling with neuropathy.
Contents
What Is Neuropathy? 
Neuropathy, also referred to as peripheral neuropathy, is a condition characterized by damage or dysfunction in the peripheral nerves that extend beyond the brain and spinal cord. These nerves play a crucial role in transmitting signals between the central nervous system and the rest of the body.
The condition can lead to a variety of symptoms, such as pain, tingling, numbness, muscle weakness, and impaired coordination. Neuropathy often occurs in the hands and feet, but it can affect other parts of the body as well. It’s important to note that neuropathy can have a wide range of causes, from underlying health conditions and injuries to genetic factors and environmental influences.
Understanding neuropathy involves recognizing its impact on nerve function and the resulting disruptions in communication between the brain, spinal cord, and various body parts. If you’re experiencing symptoms consistent with neuropathy, seeking medical evaluation is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate management.
What Are The Causes of Neuropathy?
Understanding the causes of neuropathy is pretty essential for both diagnosis and effective treatment. Here are some common causes of neuropathy:
- Diabetes: Diabetic neuropathy is one of the most prevalent causes. High blood sugar levels in diabetes can lead to nerve damage over time. This can result in symptoms such as numbness, tingling, and pain, often starting in the feet and gradually progressing to other parts of the body.
- Medications: Some medications, particularly certain chemotherapy drugs, and drugs used to treat HIV/AIDS, can cause nerve damage as a side effect. This type of neuropathy is often referred to as medication-induced neuropathy.
- Vitamin Deficiencies: Essential vitamins, especially B vitamins like B1, B6, and B12, play a crucial role in maintaining nerve health. Deficiencies in these vitamins, often due to poor diet or malabsorption issues, can lead to neuropathy symptoms.
- Alcohol Abuse: Excessive and prolonged alcohol consumption can cause alcoholic neuropathy. Alcohol’s toxic effect on nerves can result in symptoms such as numbness, pain, and weakness, usually in a symmetric pattern in the limbs.
- Autoimmune Disorders: Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and Guillain-Barré syndrome involve the immune system attacking the body’s own tissues, including nerves. This immune response can lead to nerve inflammation and damage.
- Infections: Some infections, such as shingles (herpes zoster), Lyme disease, or HIV, can directly affect nerves and cause neuropathy. The infections trigger an inflammatory response that damages nerve fibers.
- Kidney and Liver Disorders: Kidney dysfunction can lead to the accumulation of toxins in the body, which can damage nerves. Similarly, liver disorders can affect nutrient absorption and metabolism, impacting nerve health.
- Thyroid Disorders: Abnormal thyroid function, especially hypothyroidism, can lead to nerve damage. Thyroid hormones play a role in maintaining nerve function, and their imbalance can contribute to neuropathy.
How Does Physical Therapy Help Someone With Neuropathy?
Physical therapy plays a significant role in helping individuals with neuropathy manage their condition and improve overall quality of life. Here’s how physical therapy can provide valuable support and relief:
Pain Management
Physical therapists use various techniques, such as manual therapy, massage, and modalities like electrical stimulation, to target and alleviate pain associated with neuropathy. They focus on reducing discomfort and improving your ability to tolerate everyday activities.
Improving Mobility
Neuropathy can lead to muscle weakness and limited joint mobility. Physical therapists especially design exercise programs that strengthen muscles, increase flexibility and enhance overall movement. These exercises help you regain functional abilities and maintain independence.
Enhancing Balance and Coordination
Neuropathy can affect balance and coordination, increasing the risk of falls. That is why physical therapists work on specific exercises that challenge your balance and proprioception, helping you regain stability and reduce the likelihood of accidents.
Education and Self-Management
Physical therapy educates you about neuropathy, its causes, and ways to manage symptoms effectively. It also teaches techniques for proper body mechanics, posture, and movement to minimize stress on affected nerves and reduce the impact of neuropathy on your daily life.
Nerve Stimulation Techniques
Some physical therapists use nerve stimulation techniques such as transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) or neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES) to promote nerve function and reduce pain.
Sensory Re-Education
For those experiencing sensory changes, physical therapists can provide sensory re-education exercises in order to improve your ability to sense touch, temperature, and pressure.
Functional Restoration
Physical therapy focuses on restoring your ability to perform daily activities that may have been compromised due to neuropathy. By working on functional tasks, you can regain independence and confidence in your abilities.
Customized Treatment Plans
Every individual’s experience with neuropathy is unique. Physical therapists mainly assess your condition and then design personalized treatment plans tailored to your specific needs, symptoms, and goals.
Long-Term Wellness
Physical therapists empower you with strategies and tools to manage your neuropathy over the long term. They provide guidance on lifestyle modifications, exercises, and self-care practices to maintain the progress you’ve made during therapy.
Collaboration
Physical therapists often work closely with other healthcare professionals, such as neurologists and pain specialists, to ensure a comprehensive and integrated approach to your neuropathy management. By partnering with a skilled physical therapist, you can gain valuable insights, learn effective techniques, and take proactive steps toward managing your neuropathy and enhancing your overall quality of life.
When Should You Seek Physical Therapy For Neuropathy?
Here are some signs that indicate it may be time to consult a physical therapist:
- Persistent Pain: If you are experiencing persistent pain, burning sensations, or discomfort in your limbs due to neuropathy, physical therapy can help manage and alleviate these symptoms.
- Muscle Weakness: Neuropathy can lead to muscle weakness, making it challenging to perform everyday activities. If you’re having difficulty with movements that were once easy, physical therapy can help improve muscle strength and function.
- Balance and Coordination Issues: Neuropathy may impact your balance and coordination, increasing the risk of falls. If you’re feeling unsteady or have had falls or near-falls, a physical therapist can work on exercises to improve your balance and reduce fall risk.
- Numbness or Tingling: Sensations of numbness, tingling, or loss of feeling in your extremities can be signs of neuropathy. Physical therapists employ sensory re-education techniques to improve your ability to sense touch and pressure.
- Functional Limitations: If neuropathy is affecting your ability to perform daily tasks such as walking, getting up from a chair, or using your hands, physical therapy can help you regain function.
- Difficulty with Fine Motor Skills: If you’re having trouble with fine motor skills, such as buttoning clothes, picking up small objects, or writing, a physical therapist can provide exercises to improve dexterity.
- Decreased Range of Motion: Neuropathy can lead to stiffness and decreased range of motion in your joints. Physical therapists can design exercises and stretches to improve flexibility and joint mobility.
- Disrupted Sleep: If neuropathy-related symptoms are affecting your sleep quality, physical therapy techniques like relaxation exercises and positioning strategies may help improve your sleep.
- Quality of Life Impact: When neuropathy symptoms significantly impact your quality of life, causing discomfort, difficulty with daily activities, and emotional distress, seeking physical therapy can help you manage these challenges.
Some Exercises In Physical Therapy For Neuropathy
Physical therapy can offer a range of exercises that target neuropathy symptoms and help improve nerve function, strength, and mobility. Here are some exercises commonly used in physical therapy for neuropathy:
Ankle Pumps
- Sit or lie down with your legs extended.
- Gently flex your ankles, pointing your toes upward.
- Then, flex your ankles in the opposite direction, pointing your toes downward.
- Perform 2-3 sets of 10-15 repetitions.
Toe Taps:
- Sit with your feet flat on the floor.
- Lift one foot and tap your toes on the ground, then lift the other foot and tap.
- Alternate tapping each foot for 1-2 minutes.
Toe Raises:
- Sit with your feet flat on the floor.
- Lift your toes while keeping your heels on the ground.
- Lower your toes back down.
- Perform 2-3 sets of 10-15 repetitions.
Finger Taps:
- Sit comfortably with your hands resting on your thighs.
- Tap each finger on your thumb, starting with your index finger and moving to your pinky.
- Reverse the sequence and tap each finger on your thumb again.
- Perform 2-3 sets of tapping for each hand.
Ball Squeezes:
- Hold a soft ball or stress ball in your hand.
- Squeeze the ball as tightly as you can, then release it.
- Perform 2-3 sets of 10-15 repetitions for each hand.
Alphabet Foot Movements:
- Sit comfortably with your legs extended.
- Use your foot to “write” each letter of the alphabet in the air.
- Perform this exercise with both feet.
Heel-to-Toe Walk:
- Walk in a straight line, placing the heel of your front foot directly in front of the toes of your back foot.
- This exercise improves balance and proprioception.
Conclusion
Physical therapy offers a practical and effective approach to managing neuropathy. With tailored exercises, stretches, and techniques, it promotes nerve health, enhances circulation, and improves muscle strength. By seeking the guidance of skilled therapists and committing to a consistent routine, individuals can take meaningful steps towards alleviating neuropathic symptoms and enjoying a better quality of life.
Physical Therapy helps patients recover from pain. If you’re experiencing Back, Shoulder, Knee, Neck, Elbow, Hip, or Arthritis pain, a physical therapist at PhysioMantra can help: Book an online physical therapy session.