Achilles tendonitis can be a formidable foe, making even the simplest of steps a painful ordeal. If you’ve found your once-joyful activities hindered by the nagging discomfort in your heel, you’re not alone. This common condition, characterized by inflammation and irritation of the Achilles tendon, can strike anyone from avid athletes to weekend warriors, or even those who spend long hours on their feet. Join us as we delve into the intricacies of Achilles tendonitis and explore the multifaceted world of physical therapy. Discover how these tailored exercises, expert guidance, and therapeutic techniques can not only alleviate pain but also strengthen and fortify your Achilles tendon, paving the way for a vibrant and pain-free tomorrow.
Contents
What is Achilles Tendonitis?
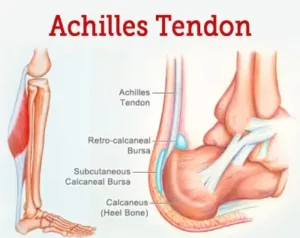 Achilles tendonitis, a common and often debilitating condition, occurs when the Achilles tendon, a thick band of tissue connecting the calf muscles to the heel bone, becomes inflamed and irritated. This condition primarily afflicts individuals engaged in repetitive activities, such as running or jumping, and those who suddenly increase their physical activity levels.
Achilles tendonitis, a common and often debilitating condition, occurs when the Achilles tendon, a thick band of tissue connecting the calf muscles to the heel bone, becomes inflamed and irritated. This condition primarily afflicts individuals engaged in repetitive activities, such as running or jumping, and those who suddenly increase their physical activity levels.
The hallmark of Achilles tendonitis is pain, typically felt as a sharp or burning sensation at the back of the heel, especially during physical activity. This discomfort can progress from a mild nuisance to a persistent hindrance if left untreated.
Common Causes of Achilles Tendonitis
Achilles tendonitis, a painful condition that affects the Achilles tendon, is often brought about by various factors related to lifestyle, physical activity, and biomechanics. Understanding these common causes can help individuals take preventive measures and make informed choices to reduce their risk of developing this painful condition.
- Overuse and Repetitive Stress: One of the primary causes of Achilles tendonitis is overuse and repetitive stress on the Achilles tendon. This can occur when individuals engage in activities that place excessive strain on the tendon without adequate rest or conditioning. Runners, especially those who suddenly increase their mileage or intensity, are particularly prone to this form of tendonitis.
- Sudden Increases in Physical Activity: Another common trigger for Achilles tendonitis is a sudden and drastic increase in physical activity. Going from a sedentary lifestyle to a highly active one, or rapidly intensifying one’s workout routine, can overload the Achilles tendon, leading to irritation and inflammation.
- Inappropriate Footwear: Wearing improper footwear during physical activities can also contribute to Achilles tendonitis. Shoes that lack proper support or do not fit well can alter the biomechanics of the foot, increasing stress on the Achilles tendon.
- Biomechanical Factors: Biomechanical issues, such as having flat feet or a high arch, can affect the distribution of force through the foot and ankle. This altered biomechanics can put undue stress on the Achilles tendon, making it more susceptible to injury.
- Tight Muscles and Tendons: Muscles and tendons that are too tight can pull on the Achilles tendon, increasing the risk of irritation and inflammation. Proper stretching and flexibility exercises are essential for maintaining tendon health.
- Age: As individuals age, the Achilles tendon may naturally weaken and become less flexible. This can make it more susceptible to injury, even with normal physical activity.
In conclusion, Achilles tendonitis can result from a combination of factors, including overuse, sudden increases in activity, inappropriate footwear, biomechanical issues, muscle tightness, and age-related changes.
Exercises for Solid Recovery
Solid recovery from Achilles tendonitis requires a structured rehabilitation program that incorporates specific exercises to strengthen the affected tendon and surrounding muscles. Here are some essential exercises to promote healing and regain strength:
Calf Raises

- Stand on the edge of a step or a sturdy platform with your heels hanging off.
- Slowly raise your heels as high as you can, then lower them below the step’s level.
- Perform this exercise both with both feet and then progress to single-leg calf raises.
Eccentric Heel Drops
- Stand on the edge of a step with your heels hanging off.
- Slowly lower your heels below the step’s level, feeling a stretch in your Achilles tendon.
- Push up using both feet, then repeat the lowering phase with one foot for a more advanced version.
Toe Raises
- Sit on a chair with your feet flat on the floor.
- Lift your toes off the ground while keeping your heels planted.
- Hold for a few seconds, then lower your toes back down.
Ankle Alphabet

- Sit on a chair or lie down with your leg extended.
- Using your big toe as a “pen,” write the alphabet in the air by moving your ankle.
- Perform this exercise to improve ankle mobility and range of motion.
Resistance Band Exercises
- Use a resistance band to perform exercises like dorsiflexion and plantarflexion resistance.
- Sit with your leg extended and loop the band around your foot, then flex and point your foot against the resistance.
Isometric Holds
- While seated, place your foot flat on the floor.
- Push your foot into the ground, engaging your calf muscle without moving your foot.
- Hold for 10-15 seconds and then relax. Repeat several times.
Balance Exercises
- Stand on one foot while keeping your balance, progressively extending the time you can stand on the affected foot.
- Use a balance board or foam pad to challenge your stability further.
Stretching Exercises
- Perform gentle stretches for the calf muscles and Achilles tendon.
- Hold each stretch for 15-30 seconds, repeating multiple times.
Always consult with a physical therapist or healthcare professional before starting any exercise program for Achilles tendonitis. And gradually increase the intensity and duration of these exercises as your condition improves to promote a solid and lasting recovery.
Effective Treatments for Achilles Tendonitis

Achilles tendonitis can be a painful and limiting condition, but several effective treatments can help alleviate symptoms and promote healing. Treatment approaches often involve a combination of conservative measures to manage pain and inflammation, along with rehabilitation to strengthen the Achilles tendon and prevent future issues. Here are some effective treatments for Achilles tendonitis:
Rest and Activity Modification:
- Initially, it’s crucial to reduce or modify activities that exacerbate the condition. Therefore, avoid high-impact activities like running or jumping.
- Rest allows the tendon to heal and inflammation to subside.
Ice Application:
- Applying ice to the affected area for 15-20 minutes several times a day can help reduce inflammation and relieve pain.
- Always use a barrier, like a cloth or towel, between the ice and your skin to prevent frostbite.
Anti-Inflammatory Medications:
- Over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), like ibuprofen, can help reduce pain and inflammation. Consult a healthcare professional before using them.
Physical Therapy:
- A physical therapist can design a customized exercise program to strengthen the Achilles tendon and calf muscles.
- Therapeutic modalities such as ultrasound and electric stimulation may be used to reduce inflammation and promote healing.
Orthotics and Supportive Footwear:
- Custom or over-the-counter orthotic inserts can correct biomechanical issues and provide better arch support.
- Wearing appropriate footwear with cushioning and arch support can help reduce stress on the Achilles tendon.
Heel Lifts:
- In some cases, using heel lifts in your shoes can reduce strain on the Achilles tendon and provide relief.
Night Splints:
- Night splints hold the foot in a dorsiflexed position during sleep, helping to stretch the calf and Achilles tendon.
Shockwave Therapy:
- Extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT) is a non-invasive procedure that uses shockwaves to stimulate blood flow and promote tissue healing.
Corticosteroid Injections:
- In severe cases with persistent pain and inflammation, a healthcare professional may recommend corticosteroid injections to reduce inflammation.
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy:
- PRP therapy involves injecting a concentrated form of the patient’s blood into the affected area to promote healing.
Surgery (in rare cases):
- Surgery is typically considered only when conservative treatments have failed. It may involve removing damaged tissue or repairing the tendon.
The choice of treatment depends on the severity of the condition and individual factors. It’s essential to consult a healthcare provider or orthopedic specialist for an accurate diagnosis and a personalized treatment plan. Early intervention and adherence to recommended treatments and exercises can significantly improve the prognosis for Achilles tendonitis.
Physical Therapy for Achilles Tendonitis
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in the rehabilitation of Achilles tendonitis. A well-structured physical therapy program can help reduce pain, promote healing, and strengthen the Achilles tendon and surrounding muscles. Here’s an overview of what physical therapy for Achilles tendonitis typically entails:
- Assessment and Evaluation: The first step in physical therapy is a thorough assessment by a physical therapist. They will evaluate your condition, including the severity of your Achilles tendonitis, any contributing factors, and your overall physical function.
- Pain Management: Initially, the focus may be on managing pain and reducing inflammation. Physical therapists may use techniques such as ice, ultrasound, or electrical stimulation to alleviate pain and swelling.
- Range of Motion Exercises: Gentle exercises to improve ankle joint mobility and flexibility may be prescribed. These can include ankle circles, ankle pumps, and gentle calf stretches.
- Strengthening Exercises: Strengthening exercises for the calf muscles, especially the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles, are a fundamental component of Achilles tendonitis rehabilitation. Exercises like calf raises, eccentric heel drops, and resisted plantarflexion help rebuild strength.
- Eccentric Exercises: Eccentric strengthening exercises, in particular, are highly effective for Achilles tendonitis. Eccentric heel drops, where you lower your heel below a step or platform, help load the tendon and promote healing.
- Balance and Proprioception Training: Improving balance and proprioception (awareness of your body’s position) is essential to prevent future injuries. Balance exercises on one leg or on unstable surfaces can be incorporated.
- Gait Analysis: Physical therapists may assess your walking and running mechanics to identify any abnormalities that may contribute to Achilles tendonitis. They can then provide guidance on correcting these issues.
- Modalities: Modalities such as heat, ice, ultrasound, or electrical stimulation may be used to reduce pain and inflammation during your sessions.
- Education: Physical therapists provide education on proper footwear, activity modification, and home exercises to ensure you continue to make progress between sessions.
- Progressive Loading: As your condition improves, the physical therapist will gradually increase the intensity of your exercises to challenge the Achilles tendon and calf muscles.
- Return-to-Activity Plan: Your physical therapist will work with you to establish a gradual return-to-activity plan, ensuring you can safely resume your desired level of physical activity without risking re-injury.
- Monitoring and Adjustments: Throughout the course of your physical therapy, your progress will be closely monitored. The therapist may make adjustments to your treatment plan based on how you respond to the exercises and interventions.
It’s important to adhere to the prescribed exercises and recommendations from your physical therapist consistently. Achilles tendonitis recovery can take time, and patience is essential.
Conclusion
In short, Achilles tendonitis can be a challenging condition, but with the right approach, recovery is within reach. Physical therapy for Achilles tendonitis offers a tailored and effective path to healing. Through a combination of targeted exercises, pain management strategies, and expert guidance, individuals can regain strength and mobility in their Achilles tendon while minimizing the risk of future injuries.
Remember, the key to a solid recovery lies in patience and commitment. By diligently following your physical therapy plan and making necessary lifestyle adjustments, you can unlock the door to pain-free movement and enjoy the activities you love once again. If you’re dealing with Achilles tendonitis, don’t hesitate to seek professional guidance from a physical therapist who can provide you with a personalized roadmap to recovery. Your Achilles deserves the best care, and physical therapy is here to help you achieve just that.
If you’re experiencing Back, Shoulder, Knee, Neck, Elbow, Hip, or Arthritis pain, physical therapist at PhysioMantra can help: Book an online physical therapy session.



