Golfer’s elbow, medically known as medial epicondylitis, is a common condition that causes pain and discomfort on the inner side of the elbow. Despite its name, this condition doesn’t solely affect golfers; it can trouble anyone who frequently uses their forearm muscles. In this article, we’ll delve into the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, prevention, and treatment options for golfer’s elbow. Whether you’re a seasoned golfer or engage in repetitive arm movements, understanding this condition is essential to maintain your overall health and well-being.
Contents
What is Golfer’s Elbow?
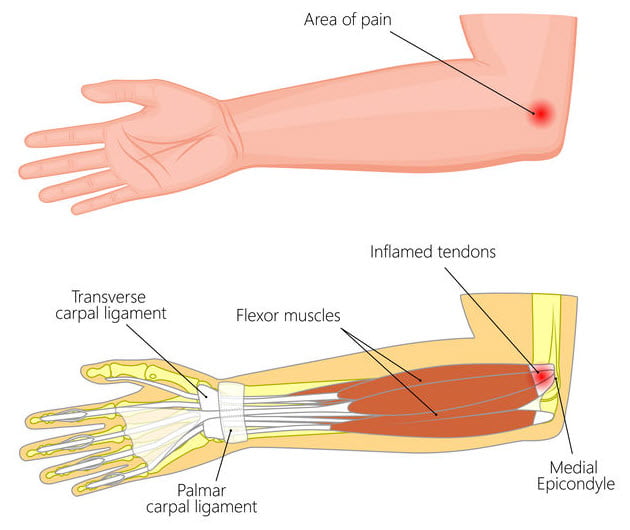
Golfer’s elbow is a form of tendinitis, which involves the inflammation of the tendons that connect the forearm muscles to the bony bump inside the elbow, called the medial epicondyle. The repetitive stress on these tendons leads to micro-tears and subsequent pain and tenderness.
To better comprehend the golfer’s elbow, it’s essential to grasp the anatomy of the affected area. The forearm muscles responsible for gripping and flexing the wrist are connected to the medial epicondyle through tendons. When these tendons are overused or strained, a golfer’s elbow may ensue.
Causes of Golfer’s Elbow
The primary cause of golfer’s elbow is overuse or repetitive stress on the forearm tendons, specifically those involved in wrist and finger flexion. Here are some common causes:
Repetitive Movements The primary cause of a golfer’s elbow is the repetition of specific arm and wrist movements. Activities such as golfing, racket sports, and even typing or painting can lead to overuse of the forearm muscles and subsequent strain on the tendons.
Incorrect Swing Technique In golfers, the condition can be exacerbated by an incorrect swing technique, placing excessive stress on the forearm tendons during the swing.
Overuse of the Forearm Muscles Activities that involve excessive gripping, lifting, or throwing can lead to overuse of the forearm muscles and contribute to the development of a golfer’s elbow.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
The main symptom of golfer’s elbow is pain and tenderness on the inside of the elbow, specifically at the bony bump called the medial epicondyle. The pain may radiate down the forearm towards the wrist. The severity of the pain can vary from mild discomfort to sharp, intense pain that can interfere with daily activities.
Other common symptoms include
- Weakness: Weakness in the affected forearm, making it difficult to grip or lift objects.
- Stiffness: Stiffness in the elbow joint, especially after periods of rest or in the morning.
- Worsening Pain: Pain that worsens with gripping, squeezing, or flexing the wrist and fingers.
- Numbness or Tingling: Some individuals may experience numbness or tingling sensations in the ring and little fingers, though this is less common.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing a golfer’s elbow typically involves a combination of a thorough medical history, physical examination, and sometimes imaging tests. During the physical examination, the doctor will look for signs of tenderness, swelling, and range of motion in the affected elbow. They may also assess grip strength and test for any neurological symptoms like numbness or tingling.
Imaging tests such as X-rays may be ordered to rule out other potential causes of elbow pain, such as fractures or arthritis. However, X-rays are often normal in cases of a golfer’s elbow since it primarily affects soft tissues like tendons.
Preventive Measures

Preventing golfer’s elbow (medial epicondylitis) involves taking measures to reduce the strain on the forearm tendons and promoting overall forearm strength and flexibility. Here are some preventive measures you can take:
Proper Warm-up and Stretching Engaging in proper warm-up exercises and stretching before physical activities can help reduce the risk of a golfer’s elbow.
Strengthening Exercises Incorporating specific strengthening exercises for the forearm muscles can increase their resilience and lower the likelihood of injury.
Correct Golfing Technique For golfers, adopting the correct swing technique and seeking professional instruction can significantly reduce the strain on the forearm tendons.
Golfer’s Elbow Treatment Options
The treatment for golfer’s elbow (medial epicondylitis) typically involves a combination of conservative measures to relieve pain, reduce inflammation, and promote healing. In most cases, surgery is not necessary, and the condition can be effectively managed with non-invasive treatments. Here are some common treatment options:
Rest and Ice Initially, resting the affected arm and applying ice packs can help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation.
Physical Therapy Physical therapy sessions may include a range of motion exercises, massage, and techniques to strengthen the forearm muscles.
Medications Over-the-counter pain medications can offer temporary relief from pain and inflammation.
Corticosteroid Injections In some cases, corticosteroid injections may be administered to reduce inflammation and provide relief.
Exercises for Rehabilitation

Rehabilitation exercises for golfer’s elbow focus on strengthening the forearm muscles, improving flexibility, and gradually increasing the load on the affected tendons to promote healing and prevent recurrence. Here are some effective exercises for rehabilitation:
- Wrist Flexor Stretch:
- Extend your affected arm straight out in front of you, with your palm facing up.
- Use your other hand to gently bend your wrist backward until you feel a stretch in the forearm.
- Hold the stretch for 15-30 seconds and repeat 2-3 times on each side.
- Wrist Extensor Stretch:
- Extend your affected arm straight out in front of you, with your palm facing down.
- Use your other hand to gently bend your wrist downward until you feel a stretch in the forearm.
- Hold the stretch for 15-30 seconds and repeat 2-3 times on each side.
How to Return to Golfing Safely
Returning to golfing safely after experiencing golfer’s elbow (medial epicondylitis) or any other injury requires a gradual and cautious approach. Here are some steps you can follow to ensure a safe return to golfing:
- Obtain Medical Clearance: Before resuming golf activities, consult with your healthcare provider or physical therapist. They can evaluate your condition, assess your progress in rehabilitation, and provide specific recommendations for returning to golf.
- Warm-Up: Prior to each golf session, warm up your body and specifically target your forearms with gentle stretching exercises. This helps improve blood flow and prepares your muscles and tendons for the activity.
- Start with Short Sessions: Begin with shorter golf sessions, and gradually increase the duration as your elbow tolerates the activity. Don’t push yourself too hard initially to avoid re-injury.
- Use Proper Technique: Focus on using proper form and technique while swinging to minimize stress on your forearm tendons. Consider taking lessons with a golf professional who can help you refine your swing mechanics.
- Modify Your Grip: Experiment with adjusting your grip to reduce strain on the affected elbow. Avoid gripping the club too tightly, which can exacerbate symptoms.
Alternative Therapies for Golfer’s Elbow
Here are some alternative therapies that may be considered:
- Acupuncture: Acupuncture involves the insertion of thin needles into specific points on the body to promote healing and pain relief. Some individuals with golfer’s elbow have reported reduced pain and improved function after acupuncture sessions.
- Massage Therapy: Deep tissue massage and myofascial release techniques can help relax tight forearm muscles and improve blood flow to the affected area. Massage therapy may alleviate some of the pain associated with golfer’s elbow.
- Chiropractic Care: Chiropractic adjustments may help restore joint function and reduce tension in the surrounding muscles. Some people find relief from golfer’s elbow through chiropractic treatment.
- Shock Wave Therapy: Extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT) is a non-invasive treatment that uses shock waves to promote healing in damaged tissues. It has been used to treat various musculoskeletal conditions, including golfer’s elbow.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: PRP therapy involves injecting a concentrated solution of the patient’s own platelets into the affected area to stimulate tissue repair and reduce inflammation.
Tips for Golfers to Avoid Golfer’s Elbow

To prevent golfer’s elbow (medial epicondylitis) and reduce the risk of developing this condition, golfers can follow these tips:
- Warm-Up: Always warm up your muscles before starting your golf game. Perform gentle stretching exercises for the forearm, wrist, and shoulders to prepare your muscles for the repetitive motions involved in golf swings.
- Proper Grip: Ensure you have a proper grip on the golf club. A grip that is too tight can place excessive strain on the forearm tendons, increasing the risk of injury. Maintain a relaxed grip throughout your swing.
- Use Correct Technique: Work with a golf professional to develop and maintain proper swing mechanics. A correct technique will help distribute the forces evenly across your body, reducing the strain on your elbows.
- Strengthen Forearm Muscles: Engage in forearm strengthening exercises to improve the strength and endurance of the muscles that support your golf swing. Exercises like wrist curls and reverse wrist curls can be beneficial.
- Take Breaks: Avoid excessive golfing without adequate breaks. Give your forearm muscles time to rest and recover between rounds or practice sessions.
- Alternate Activities: If you play golf frequently, consider alternating golfing days with other activities to reduce the repetitive stress on your forearms.
Conclusion
Golfer’s elbow can be a bothersome condition for avid golfers and individuals with repetitive forearm movements. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is vital for both prevention and management. By following preventive measures, seeking appropriate treatment, and incorporating alternative therapies, you can overcome golfer’s elbow and get back to enjoying your favorite activities pain-free.
If you’re experiencing Elbow pain, physical therapy for elbow pain at PhysioMantra can help: Book an online physical therapy session.