Elbow tendonitis, also known as tennis elbow or lateral epicondylitis, is a painful condition that affects the tendons surrounding the elbow joint. It is a common injury that often occurs due to overuse or repetitive strain on the forearm muscles and tendons. In this article, we will explore effective treatment options, lifestyle modifications, and preventive measures to manage and recover from elbow tendonitis.
Contents
Understanding Elbow Tendonitis

Elbow tendonitis, also known as lateral epicondylitis or tennis elbow, is a condition characterized by inflammation and pain in the tendons that attach to the lateral epicondyle of the elbow. Despite its common name “tennis elbow,” this condition can affect anyone, not just tennis players. It typically occurs due to overuse or repetitive stress on the forearm muscles and tendons.
Causes:
- Repetitive motions: Activities that involve repeated movements of the wrist and forearm, such as playing tennis, golf, typing, painting, or using hand tools, can strain the tendons and lead to inflammation.
- Poor technique: Incorrect form or technique during sports or manual tasks can put excessive stress on the tendons, contributing to tendonitis.
- Age-related degeneration: As people age, tendons may lose some of their elasticity and become more prone to injury and inflammation.
Symptoms:
- Pain and tenderness on the outer side of the elbow, which may extend down the forearm.
- Weakness in the affected arm and difficulty gripping objects.
- Pain is exacerbated by activities that involve wrist movement or gripping.
- Stiffness and discomfort in the elbow, particularly in the morning.
Diagnosis of Elbow Tendonitis
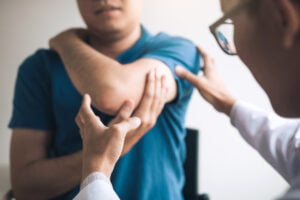
The diagnosis of elbow tendonitis, also known as lateral epicondylitis or tennis elbow, typically involves a thorough medical history review, physical examination, and sometimes imaging tests to rule out other possible causes of the symptoms. Here’s how the diagnosis process usually works:
- Physical Examination: The doctor will then perform a physical examination of the affected arm and elbow. They will look for signs of tenderness, swelling, or redness around the lateral epicondyle, which is the bony bump on the outer side of the elbow. They may also check for any weakness in the forearm muscles and assess your range of motion.
- Specific Tests: During the physical examination, the doctor may conduct specific tests to provoke pain and assess the condition further. One common test is the “Cozen’s test,” where the patient is asked to extend their wrist against resistance, stressing the affected tendons. If this maneuver reproduces the pain on the outer side of the elbow, it may suggest lateral epicondylitis.
- Imaging: In most cases, imaging tests like X-rays are not necessary for diagnosing elbow tendonitis since it does not show up on standard X-rays. However, the doctor might recommend an MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) or ultrasound if they suspect other potential issues, such as a tear in the tendons, or if symptoms persist despite conservative treatments.
Traditional Treatments for Elbow Tendonitis
Traditional treatments for elbow tendonitis (lateral epicondylitis or tennis elbow) are focused on relieving pain, reducing inflammation, and promoting healing. These treatments are typically non-invasive and can be effective in many cases. Here are some of the traditional treatment options:
- Rest: One of the essential steps in treating tendonitis is to allow the affected arm and elbow to rest. Avoiding activities that aggravate the condition can help prevent further strain on the tendons and promote healing.
- Ice: Applying ice packs to the affected area for about 15-20 minutes several times a day can help reduce inflammation and alleviate pain. Be sure to wrap the ice pack in a thin cloth to prevent direct contact with the skin.
- Pain Relief Medication: Over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen or naproxen, can help manage pain and reduce inflammation. Always follow the recommended dosage and consult a healthcare professional if you have any health conditions or concerns.
Physical Therapy for Elbow Tendonitis
Here are some common techniques and exercises used in physical therapy for elbow tendonitis:
- Range of Motion Exercises: Gentle range of motion exercises for the elbow and wrist can help improve flexibility and reduce stiffness in the affected area.
- Eccentric Strengthening Exercises: Eccentric exercises involve controlled lengthening of the forearm muscles while resisting the load. These exercises are commonly used for tennis elbow and can help to rebuild strength and reduce pain. Examples include wrist curls with a dumbbell, eccentric wrist extension exercises, and pronation/supination exercises.
- Isometric Strengthening Exercises: Isometric exercises involve muscle contractions without joint movement. These exercises can help build strength in the forearm muscles without putting excessive strain on the inflamed tendons.
- Therapeutic Ultrasound: Ultrasound therapy is sometimes used by physical therapists to promote blood circulation and stimulate healing in the affected area.
- Manual Therapy: Hands-on techniques like massage and soft tissue mobilization can help reduce muscle tension, improve blood flow, and alleviate pain.
Ergonomics and Workstation Setup

Ergonomics and proper workstation setup are crucial for preventing and reducing the risk of injuries and musculoskeletal disorders, including conditions like elbow tendonitis. An ergonomic workstation is designed to promote a comfortable and efficient work environment, reducing strain on the body during prolonged periods of work. Here are some essential ergonomic tips for setting up your workstation:
Chair:
- Use an adjustable chair that provides proper lumbar support to maintain the natural curve of your lower back.
- Adjust the seat height so that your feet are flat on the floor and your knees are at a 90-degree angle or slightly lower.
- Ensure your thighs are parallel to the ground, and there’s a small gap (about 2-3 fingers wide) between the back of your knees and the chair.
Desk:
- Position your desk at a height where your forearms are parallel to the floor when typing or using the mouse.
- Keep your wrists in a neutral position, neither flexed upward nor downward, while typing.
Keyboard and Mouse:
- Place your keyboard and mouse at a comfortable distance from your body, so you don’t need to reach or overextend.
- Use a keyboard with a low-force key activation to reduce strain on your fingers.
- Consider using an ergonomic split keyboard or an adjustable keyboard tray to keep your wrists in a neutral position.
Monitor:
- Position your monitor directly in front of you at eye level, about an arm’s length away.
- The top of the screen should be at or just below eye level to prevent straining your neck and upper back.
- Tilt the monitor slightly upward, so you don’t need to bend your neck to view the screen.
Caring for Elbow Tendonitis at Home
Caring for elbow tendonitis at home involves a combination of self-care measures to alleviate pain, reduce inflammation, and support the healing process. Here are some home remedies and practices to help manage elbow tendonitis:
- Rest: Avoid activities that worsen the pain and give your affected arm adequate rest to allow the inflamed tendons to heal.
- Ice: Applying ice packs to the affected area for about 15-20 minutes, several times a day, can help reduce inflammation and provide pain relief. Be sure to wrap the ice pack in a thin cloth to avoid direct contact with the skin.
- Compression: Consider using an elbow brace or strap to provide support to the affected tendons and reduce strain during daily activities.
- Elevate: When resting, try to keep your affected arm elevated to reduce swelling and promote blood flow.
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relief: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen or naproxen, can help manage pain and reduce inflammation. Always follow the recommended dosage and consult your doctor if you have any health conditions or concerns.
Conclusion
Elbow tendonitis can be a painful and limiting condition, but with the right approach, it is possible to manage and recover effectively. Combining traditional treatments, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications can lead to positive outcomes. By taking preventive measures and seeking professional help when needed, individuals can alleviate pain and resume their regular activities.
If you’re experiencing Elbow pain, physical therapy for elbow pain at PhysioMantra can help: Book an online physical therapy session.



