When you experience pain in your elbow, it can severely limit your daily activities, hindering your ability to perform even the simplest tasks. Anterior elbow pain, pain felt on the front side of the elbow, is a common condition that affects many individuals, from athletes to office workers. In this article, we will delve into the causes, treatments, and preventive measures for anterior elbow pain.
Contents
Anatomy of the Elbow
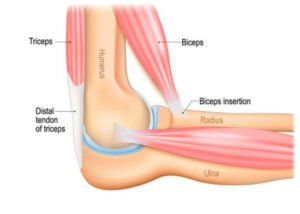
To understand anterior elbow pain, we must first familiarize ourselves with the elbow’s complex anatomy. The elbow joint consists of three bones: the humerus, radius, and ulna. It is supported by muscles, tendons, and ligaments, which allow for various movements like flexion and extension.
The muscles and tendons play a crucial role in stabilizing the joint and facilitating arm movements. When any of these components suffer damage or strain, it can lead to anterior elbow pain.
Types of Anterior Elbow Pain
Anterior elbow pain refers to pain that is felt on the front or inner side of the elbow. There are several potential causes of anterior elbow pain, including:
- Golfer’s Elbow (Medial Epicondylitis): This condition involves inflammation or irritation of the tendons on the inner side of the elbow, specifically the tendons that attach to the medial epicondyle. It is often caused by repetitive wrist flexion or forceful gripping activities.
- Biceps Tendonitis: Inflammation of the biceps tendon can cause pain in the front of the elbow. This condition is common in people who perform repetitive overhead activities.
- Ulnar Collateral Ligament (UCL) Injury: The UCL is a ligament on the inner side of the elbow that stabilizes the joint during throwing motions. Overuse or traumatic injuries, especially in athletes who engage in throwing sports, can lead to UCL tears or sprains.
- Distal Biceps Tendon Rupture: This occurs when the tendon attaching the biceps muscle to the radius bone at the elbow tears or ruptures. It can cause sudden and severe pain in the front of the elbow.
Risk Factors
Several factors can increase the risk of developing anterior elbow pain. Engaging in repetitive arm movements or sports that involve gripping and swinging, such as golf, tennis, and weightlifting, can strain the elbow’s structures.
Certain occupations, like those involving manual labor or desk work with poor ergonomics, can also contribute to the development of elbow pain. Age-related changes and degeneration of tissues may make individuals more susceptible to anterior elbow pain.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
The symptoms of anterior elbow pain can vary depending on the underlying cause. However, some common symptoms include:
- Pain on the front or inner side of the elbow.
- Tenderness and sensitivity to touch in the affected area.
- Pain that worsens with specific activities or movements, such as gripping, lifting, or throwing.
- Swelling or inflammation around the elbow joint.
- Limited range of motion in the elbow.
- Weakness in the forearm or hand.
- Numbness or tingling sensations in the forearm or hand (if nerve compression is involved).
- Clicking or popping sensation in the elbow during movement (in some cases).
Diagnosis of Anterior Elbow Pain
Diagnosing the cause of anterior elbow pain involves a thorough medical evaluation, which may include the following steps:
- Medical History: The healthcare professional will inquire about the patient’s symptoms, when the pain started, any specific activities that trigger or worsen the pain, and any relevant medical history or previous injuries.
- Physical Examination: The doctor will perform a physical examination of the elbow to assess for signs of inflammation, tenderness, range of motion, and strength. They may also perform specific tests to evaluate the integrity of the ligaments, tendons, and nerves around the elbow joint.
- Imaging Studies: X-rays can help identify bony abnormalities, fractures, or joint degeneration. MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) or ultrasound may be ordered to visualize soft tissues like tendons, ligaments, and cartilage, which can be helpful in detecting conditions like golfer’s elbow, biceps tendonitis, or UCL injuries.
- Electromyography (EMG) or Nerve Conduction Studies: These tests may be performed if there are signs of nerve compression or injury to assess the function of the nerves and muscles in the forearm.
Treatment Options

The treatment options for anterior elbow pain depend on the underlying cause of the pain. Here are some common treatment approaches for various conditions that can cause anterior elbow pain:
- Rest and Activity Modification: One of the first steps in treating anterior elbow pain is to rest the affected arm and avoid activities that exacerbate the pain. Depending on the specific condition, certain movements or sports may need to be modified or temporarily stopped to allow the elbow to heal.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy can be beneficial in many cases of anterior elbow pain. Therapists can design exercises to improve flexibility, strength, and stability around the elbow joint. They may also use techniques like ultrasound or electrical stimulation to promote healing.
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Over-the-counter NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen or naproxen, can help reduce pain and inflammation associated with conditions like golfer’s elbow or biceps tendonitis. However, long-term or excessive use of NSAIDs should be avoided, as they can have side effects.
- Brace or Splint: In some cases, wearing a brace or splint can provide support to the elbow and help alleviate strain on the affected structures during the healing process.
Preventive Measures
Preventive measures are essential to reduce the risk of developing anterior elbow pain or to prevent the recurrence of the condition after treatment. Here are some preventive measures you can take:
- Proper Warm-up and Stretching: Before engaging in any physical activity, especially those that involve repetitive arm movements, perform a thorough warm-up and stretching routine. This helps prepare the muscles and tendons for the activity and reduces the risk of overuse injuries.
- Strength Training: Regularly engage in strength training exercises that target the muscles around the elbow, forearm, and shoulder. Strong muscles provide better support to the elbow joint and can help prevent injuries.
- Correct Technique and Form: Whether it’s sports, weightlifting, or daily activities, use the correct technique and form to avoid unnecessary strain on the elbow joint. If you’re unsure about proper form, consider consulting a coach or a qualified instructor.
- Avoid Overuse: Be mindful of repetitive activities that put stress on the elbow, such as excessive typing, gripping, or throwing. Take regular breaks, and if possible, rotate tasks to avoid prolonged strain on the elbow.
- Use Proper Equipment: Make sure that sports equipment, tools, and utensils you use are appropriately sized and designed for your body and the activity. For example, using a racket with a grip that’s too large can increase the risk of tennis elbow.
Living with Anterior Elbow Pain
Living with anterior elbow pain can be challenging, but there are strategies and lifestyle adjustments that can help you manage the discomfort and improve your quality of life. Here are some tips for living with anterior elbow pain:
- Rest and Avoid Aggravating Activities: Give your elbow sufficient time to rest and avoid activities that worsen the pain. Overusing the affected arm can delay healing and exacerbate the condition.
- Physical Therapy and Exercises: Work with a physical therapist to learn exercises that can improve the strength, flexibility, and stability of the elbow joint and surrounding muscles. A tailored exercise program can help promote healing and prevent further injury.
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain medications, like acetaminophen or NSAIDs (if suitable for you), can provide temporary relief. Follow the recommended dosage and speak to your doctor before using them regularly.
- Use Ice and Heat Therapy: Applying ice packs or using heat pads can help reduce inflammation and alleviate pain. Ice is beneficial in the acute phase of an injury, while heat can provide relief for chronic conditions.
- Bracing or Splinting: Using a brace or splint can provide support to the elbow and limit movements that aggravate the pain. Consult with a healthcare professional to ensure you use the appropriate type of brace.
Recovery and Rehabilitation

Gradual return to activities is a vital aspect of the recovery process.
- Rushing back into physical activities without proper healing can lead to reinjury or worsen the condition.
- Following healthcare providers’ recommendations for exercises and activities can help ensure a successful recovery.
- Regular follow-up appointments are essential to monitor progress and address any concerns that may arise during the rehabilitation period.
- Preventing recurrence is also crucial, and individuals should continue with exercises and preventive measures even after the pain subsides.
Addressing Anterior Elbow Pain in Athletes
For athletes, anterior elbow pain can be particularly concerning, as it can significantly impact their performance and career. Specific sports have unique risk factors, and understanding sports-specific considerations can aid in preventing and managing elbow pain.
An athlete’s mindset during the recovery process plays a vital role, as a positive outlook and patience are essential for a successful return to play.
Having a supportive team, including coaches, trainers, and medical professionals, can also contribute to the athlete’s overall recovery and well-being.
Conclusion
In conclusion, anterior elbow pain is a common condition that can affect individuals from various backgrounds. Understanding the anatomy of the elbow, types of anterior elbow pain, and risk factors is crucial in addressing the issue effectively. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are key to a successful recovery. By incorporating preventive measures and seeking professional help when needed, individuals can better manage and alleviate anterior elbow pain, allowing them to lead active and fulfilling lives.
If you’re experiencing Elbow pain, physical therapy for elbow pain at PhysioMantra can help: Book an online physical therapy session.



