Bicep tendonitis is a painful condition that affects the bicep tendons, causing discomfort and limiting the range of motion in the shoulder. These tendons are essential for the proper functioning of the arm, as they connect the bicep muscles to the bones in the shoulder. In this article, we will delve into the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for bicep tendonitis, as well as tips for prevention and recovery.
Contents
Causes of Bicep Tendonitis
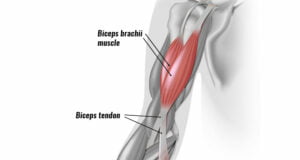
Biceps tendonitis, also known as bicipital tendonitis, is a condition characterized by inflammation or irritation of the biceps tendon. The biceps tendon connects the biceps muscle to the shoulder and elbow joints, and repetitive or excessive use of the biceps can lead to this condition. Some of the common causes of biceps tendonitis include:
- Overuse or repetitive strain: Repeatedly performing activities that involve the biceps muscle, such as weightlifting, throwing, or repetitive lifting, can strain the biceps tendon and lead to inflammation.
- Muscle imbalances: Imbalances in the muscles around the shoulder and arm can put extra stress on the biceps tendon, leading to inflammation.
- Poor technique or form: Incorrect body mechanics during physical activities can contribute to biceps tendonitis by placing excessive stress on the tendon.
- Aging: As people age, tendons naturally become less flexible and more prone to injury. This can make the biceps tendon more susceptible to inflammation.
- Sudden trauma or injury: A sudden force or injury to the biceps, such as a fall or direct blow to the arm, can cause biceps tendonitis.
Symptoms of Bicep Tendonitis
Biceps tendonitis is characterized by pain and discomfort in the front of the shoulder and upper arm. The symptoms can vary in intensity and may worsen with certain movements or activities involving the affected arm. Common symptoms of biceps tendonitis include:
- Shoulder Pain: Pain is typically felt at the front of the shoulder, near the biceps muscle and the top of the upper arm. The pain may be described as a dull ache or a sharp, stabbing sensation.
- Arm Weakness: You might experience weakness in the affected arm, particularly when attempting to lift or carry objects or perform certain movements.
- Pain with Movement: Pain often worsens with certain arm movements, especially those that involve bending the elbow or raising the arm overhead.
- Pain at Night: Some individuals with biceps tendonitis may experience increased pain and discomfort at night, which can disrupt sleep.
- Tenderness and Swelling: There may be tenderness and swelling in the front of the shoulder where the biceps tendon attaches.
- Painful Clicking or Snapping: In some cases, there may be a clicking or snapping sensation in the shoulder when moving the arm, known as crepitus.
- Limited Range of Motion: Biceps tendonitis can lead to a reduced range of motion in the affected shoulder, making certain movements challenging or painful.
Diagnosis of Bicep Tendonitis

The diagnosis of biceps tendonitis typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and, in some cases, imaging studies. Here’s how healthcare professionals diagnose biceps tendonitis:
- Medical History: The doctor will begin by taking a detailed medical history, including asking about the patient’s symptoms, the duration and pattern of pain, any previous injuries or medical conditions, and the types of activities that may aggravate or alleviate the pain.
- Physical Examination: A thorough physical examination is performed to assess the range of motion, strength, and stability of the shoulder and arm. The doctor will also palpate the shoulder to check for tenderness, swelling, or other signs of inflammation around the biceps tendon.
- Provocative Tests: During the physical examination, the doctor may perform specific maneuvers or provocative tests that aim to reproduce the pain or discomfort associated with biceps tendonitis. For example, they might perform “Speed’s test” or “Yergason’s test” to assess the integrity of the biceps tendon.
Prevention of Bicep Tendonitis
Preventing biceps tendonitis involves adopting good practices and lifestyle habits that reduce the risk of overuse and strain on the biceps tendon. Here are some tips to help prevent biceps tendonitis:
- Warm-up and Stretching: Always warm up before engaging in physical activities that involve the arms, especially those that require repetitive arm movements. Perform gentle stretching exercises to increase flexibility in the shoulders and arms.
- Proper Technique: Ensure that you use the proper form and technique while engaging in sports, weightlifting, or any activity that involves the arms. Avoid excessive force or improper body mechanics that can strain the biceps tendon.
- Strength and Flexibility Training: Include regular strength training and flexibility exercises in your fitness routine. Strengthening the muscles around the shoulder and upper arm can help support the biceps tendon and reduce the risk of injury.
- Avoid Overuse: Allow adequate rest and recovery between intense workouts or repetitive arm movements. Avoid performing the same exercises or activities for extended periods without breaks.
Home Remedies and Self-Care
Here are some home remedies and self-care measures you can try:
- Rest: Give your affected arm and shoulder adequate rest to allow the inflamed biceps tendon to heal. Avoid activities that worsen the pain or strain the tendon.
- Ice Therapy: Apply ice packs wrapped in a thin cloth to the affected area for about 15-20 minutes several times a day. Ice can help reduce inflammation and provide pain relief.
- Compression: If there is swelling, consider using a compression bandage or wrap to reduce swelling and provide support. Ensure the bandage is not too tight to avoid compromising blood circulation.
- Elevation: Elevate your arm whenever possible, especially when resting or sleeping. This can help reduce swelling and promote healing.
- Gentle Exercises: Once the acute pain subsides, perform gentle range-of-motion exercises to maintain flexibility in the shoulder joint. Avoid high-impact or strenuous exercises until the tendonitis is fully healed.
Medical Treatments
Here are some common medical treatments for biceps tendonitis:
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Over-the-counter NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen or naproxen, can help reduce pain and inflammation associated with biceps tendonitis. Always follow the recommended dosage and consult with a healthcare professional if you have any underlying health conditions or are taking other medications.
- Physical Therapy: A physical therapist can create a tailored exercise program to strengthen the muscles around the shoulder and improve flexibility. They may also use modalities such as ultrasound, electrical stimulation, or heat/cold therapy to aid in pain relief and promote healing.
- Corticosteroid Injections: In cases of persistent inflammation and pain, a healthcare professional may administer corticosteroid injections directly into the affected area. These injections can provide significant pain relief and reduce inflammation. However, they are usually limited to one or two injections per year due to potential side effects.
Exercises for Bicep Tendonitis

Always consult with a healthcare professional or a qualified physical therapist before starting any exercise program for biceps tendonitis. Here are some recommended exercises:
Pendulum Swings:
- Stand with your unaffected hand on a stable surface (e.g., a table or chair).
- Let your affected arm hang down naturally.
- Gently sway your arm in small circles in a clockwise and counterclockwise direction.
- Perform this exercise in a pain-free range of motion.
Isometric Bicep Contractions:
- Sit or stand with your back straight.
- Bend your affected arm at a 90-degree angle with your palm facing upward.
- Press your palm into your other hand or a wall, creating resistance but not allowing your arm to move.
- Hold for 5-10 seconds, then release. Repeat for 10-15 repetitions.
Scapular Squeezes:
- Sit or stand with your back straight and shoulders relaxed.
- Squeeze your shoulder blades together as if trying to hold a pencil between them.
- Hold the squeeze for 5-10 seconds, then relax. Repeat for 10-15 repetitions.
Wall Slides:
- Stand with your back against a wall and your feet about 6 inches away from the wall.
- Slowly slide your arms up the wall, keeping your elbows bent until they are at shoulder height.
- Slide your arms back down to the starting position.
- Perform this exercise in a controlled manner and avoid any pain.
Tips for Avoiding Bicep Tendonitis Recurrence
To avoid the recurrence of biceps tendonitis, it’s essential to make some lifestyle and activity modifications and follow good preventive practices. Here are some tips to help you prevent biceps tendonitis from coming back:
- Gradual Progression: When returning to physical activities or exercise after recovering from biceps tendonitis, start slowly and gradually increase the intensity and duration. Avoid jumping back into high-impact or strenuous activities too quickly.
- Proper Technique: Ensure that you use the correct form and technique while engaging in sports, weightlifting, or any activity that involves the arms. Seek guidance from a qualified coach or trainer if needed.
- Strength and Flexibility Training: Regularly incorporate strength training exercises that target the muscles around the shoulder, upper arm, and back. Strengthening these muscles can help support the biceps tendon and reduce the risk of injury.
- Balanced Workout Routine: Avoid overusing the same muscles or performing repetitive movements that strain the biceps. Incorporate a variety of exercises into your workout routine to distribute the workload.
- Rest and Recovery: Give your body sufficient time to recover between workouts. Adequate rest and recovery are essential for preventing overuse injuries.
Conclusion
Bicep tendonitis is a painful condition that can significantly impact daily life. Early diagnosis and appropriate care are essential for managing the symptoms effectively. Whether through self-care, non-invasive treatments, or surgical interventions, addressing bicep tendonitis promptly can lead to a faster and smoother recovery. Remember to consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice and treatment options.
If you’re experiencing Elbow pain, physical therapy for elbow pain at PhysioMantra can help: Book an online physical therapy session.



