Knee pain is a common complaint among people of all ages, and it can arise from various causes. While many focus on the front of the knee, pain at the back of the knee is also known as posterior knee pain. It is a concern that shouldn’t be overlooked. In this article, we’ll delve into the common reasons for back of knee pain, potential remedies, and tips to prevent future discomfort.
Contents
Is It Normal For The Back Of Your Knee To Hurt?
 Yes, experiencing back of knee pain, also known as posterior knee pain, is not uncommon and can be due to various causes. This region contains several structures like tendons, ligaments, and vessels that can be susceptible to injury or strain. However, while it’s normal for some people to occasionally experience pain behind the knee, it’s essential to differentiate between temporary discomfort and persistent pain.
Yes, experiencing back of knee pain, also known as posterior knee pain, is not uncommon and can be due to various causes. This region contains several structures like tendons, ligaments, and vessels that can be susceptible to injury or strain. However, while it’s normal for some people to occasionally experience pain behind the knee, it’s essential to differentiate between temporary discomfort and persistent pain.
That could signal a more severe issue. If the pain is accompanied by serious signs or lasts for an extended period, it would be prudent to seek medical advice. Sometimes, a comprehensive approach might be necessary to address the underlying cause and ensure optimal knee health.
How Do I Know If My Knee Pain Is Serious?
Differentiating between general knee pain and something more serious can be challenging. However, several signs and symptoms can indicate a more severe issue that requires prompt medical attention:
- Swelling and Inflammation
While some swelling after an injury can be typical, sudden and significant swelling or swelling that persists. This can be a sign of a severe injury like an ACL tear or meniscal injury.
- Inability to Bear Weight
If you find it challenging or impossible to put weight on your knee or walk without significant pain. Then, this could be a sign of a fracture or a severe ligament injury.
- Deformity
A visible change in the shape or alignment of your knee — such as looking crooked or out of place — may indicate a dislocation or fracture.
- Locking or Catching
If your knee locks up and won’t bend or straighten, or if it feels like it’s catching or giving way, it might be due to a meniscal tear or loose fragments of bone or cartilage.
- Persistent Pain
While most minor injuries will get better with rest and conservative treatment, persistent pain. Especially if it doesn’t improve over a week or more, should be evaluated.
- Limited Range of Motion
An inability to fully straighten or bend your knee, especially if accompanied by pain or swelling, could be a sign of a severe injury or an underlying condition.
- Signs of Infection
If you notice redness or warmth, or if the pain is accompanied by a fever or chills, it might indicate an infection in or around the knee joint.
- Popping or Audible Snap
A loud pop at the time of injury might suggest a ligament rupture, like an ACL tear.
If you experience any of these symptoms or have any concerns about the severity of your pain, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional. An accurate diagnosis, often aided by imaging tests like X-rays or MRIs, is crucial for appropriate treatment and recovery.
What Are The Common Causes of Pain Behind The Knee?
 This pain can stem from a variety of causes. Here are some of the most common:
This pain can stem from a variety of causes. Here are some of the most common:
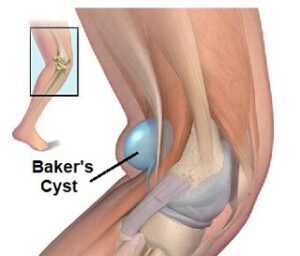
1. Baker’s Cyst (Popliteal Cyst)
This is a fluid-filled cyst that forms at the back of the knee, often due to inflammation or other underlying knee conditions like arthritis or meniscal tears. It can cause swelling and discomfort behind the knee.
2. Hamstring Tendinitis
Overuse or strain of the hamstring muscles can lead to inflammation of the tendons. That is causing pain in the back of the knee.
3. Calf Strains
The calf muscles are situated close to the knee, and an injury or strain here can lead to pain at the back of the knee.
4. Meniscal Tears
While meniscal injuries often cause pain at the front or side of the knee, certain types of tears can cause pain behind the knee as well.
5. Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
A blood clot in the veins located deep within the legs can cause pain behind the knee. This is a serious condition that requires immediate medical attention, as the clot could travel to the lungs and become life-threatening.
6. Arthritis
While arthritis commonly causes pain at the front or sides of the knee, it can also result in pain behind the knee. Especially if there’s swelling or a Baker’s cyst associated with it.
7. Hyperextension of the Knee
Overstretching or bending the knee backward can cause posterior knee pain, especially if ligaments are strained.
8. Ligament Injuries
Though less common, injuries to the posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) or the popliteus tendon can lead to pain at the back of the knee.
It’s essential to accurately diagnose the cause of pain behind the knee to ensure appropriate treatment. If you’re experiencing persistent posterior knee pain, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or orthopedic specialist for a proper evaluation.
How Do I Fix The Pain Behind My Knee?
 The approach to fixing pain behind the knee depends on the underlying cause. Here are some general guidelines and potential treatments that you can consider. But remember that it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and personalized advice:
The approach to fixing pain behind the knee depends on the underlying cause. Here are some general guidelines and potential treatments that you can consider. But remember that it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and personalized advice:
Rest and Avoid Overuse
If you’ve been engaging in activities that strain the knee, such as excessive running or jumping, giving your knee adequate rest is crucial. Resting allows the tissues to heal and inflammation to subside. Avoiding activities that aggravate the pain will prevent further damage.
Apply Ice and Compression
Ice packs help reduce inflammation by constricting blood vessels and numbing the area. Apply an ice pack wrapped in a thin cloth for about 15-20 minutes every few hours. Compression wraps provide gentle pressure to the area, helping to control swelling. Make sure not to wrap too tightly, as it can impede circulation.
Elevate the Leg
Elevating the leg above the level of your heart whenever possible reduces swelling by allowing fluids to drain away from the area. Use pillows or cushions to prop up your leg while resting or sleeping.
Physical Therapy
A physical therapist can evaluate your knee’s condition and design a personalized exercise program. Strengthening exercises for the muscles around the knee, along with flexibility exercises, can improve joint stability and reduce pain.
Medications
Non-prescription nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen or naproxen can help relieve pain and inflammation. However, it’s important not to rely on these medications for long periods without medical supervision, as they can have side effects.
Corticosteroid Injections
If conservative treatments don’t provide relief, a doctor might recommend corticosteroid injections. These injections deliver powerful anti-inflammatory medication directly into the affected area, providing temporary relief. However, they’re not suitable for long-term use due to potential side effects.
Surgical Intervention
In cases where there’s structural damage like large Baker’s cysts, severe ligament tears, or certain fractures, surgical intervention might be necessary. Consult an orthopedic specialist to determine if surgery is the best option for your situation.
Addressing Underlying Conditions
If your pain is a symptom of an underlying condition, such as arthritis or deep vein thrombosis, treating the root cause is essential. Treating the condition often alleviates the pain. Consult with a healthcare professional to manage these conditions appropriately.
Remember, every individual’s situation is unique. Consulting a healthcare professional is vital for accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment. Attempting self-treatment without a proper understanding of the underlying issue can worsen the condition.
What Are Some Ways To Prevent Back of Knee Pain?
 Preventing this pain involves a combination of lifestyle adjustments, proper techniques, and maintaining overall knee health. Here are some strategies to help prevent pain behind the knee:
Preventing this pain involves a combination of lifestyle adjustments, proper techniques, and maintaining overall knee health. Here are some strategies to help prevent pain behind the knee:
- Warm Up and Stretch
Prior to engaging in physical activities or exercise, warm up your muscles with light aerobic activity. And then perform dynamic stretches to prepare your knee for movement.
- Proper Technique
If you’re involved in sports or activities that stress the knee, such as running or cycling, ensure you’re using the correct technique to minimize strain on the knee joint.
- Gradual Progression
When starting a new exercise routine or increasing the intensity of your workouts, do so gradually to allow your knee to adapt to the increased demands.
- Strength Training
Incorporate exercises that strengthen the muscles around the knee, such as quadriceps and hamstrings. This will help to provide better support to the joint.
- Flexibility Exercises
Regularly stretch the muscles around the knee, including the hamstrings and calf muscles, to maintain flexibility and reduce the risk of strain.
- Proper Footwear
Wear shoes that offer proper support and cushioning for your activities. Consult a specialist if you need recommendations for sports-specific footwear.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight
Excess body weight can place additional stress on the knee joint. Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the risk of knee pain and related issues.
- Stay Hydrated
Proper hydration supports joint health and reduces the risk of cramping and muscle strains.
- Listen to Your Body
Pay attention to any discomfort or pain. If you feel pain, especially behind the knee, stop the activity and rest. Ignoring pain can lead to more severe injuries.
- Maintain Good Posture
Proper posture while sitting, standing, and walking can help distribute weight evenly and reduce strain on the knee joint.
- Use Supportive Braces or Tape
In certain cases, using knee braces or taping techniques can provide additional support and stability. Especially during sports or activities.
Implementing these preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of pain and help you maintain an active and pain-free lifestyle.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding and addressing the pain is essential for maintaining overall knee health and ensuring an active, pain-free lifestyle. From Baker’s cysts and hamstring tendinitis to overuse injuries and underlying conditions like arthritis, the causes of posterior knee pain can vary widely. By adopting a holistic approach, individuals can mitigate the risk of pain, while seeking medical guidance and professional care when necessary.
Prioritizing rest, listening to one’s body, and incorporating proper footwear and biomechanics are key to preventing pain in the knee. If you’re experiencing Knee pain, physical therapy for knee pain at PhysioMantra can help: Book an online physical therapy session.



