Quadriceps tendonitis, a prevalent ailment among athletes and active individuals, arises from the inflammation or injury of the tendon connecting the quadriceps muscles to the knee cap. Often resulting from overuse, this condition can lead to pain and hinder daily activities if left untreated. This article delves into effective treatment strategies and preventive measures to ensure a quick recovery and reduce the risk of recurrence.
Contents
What Are Some Quadriceps Tendonitis Treatments?
 The treatment approach depends on the severity of the condition, the patient’s overall health, and their specific needs and goals. Here are the main treatment options for quadriceps tendonitis:
The treatment approach depends on the severity of the condition, the patient’s overall health, and their specific needs and goals. Here are the main treatment options for quadriceps tendonitis:
- Activity Modification:
One of the first recommendations is to reduce or stop the activities causing or aggravating tendonitis. This gives the injured tendon a chance to heal.
- Non-steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs):
Medications like ibuprofen or naproxen can decrease pain and inflammation. However, they should be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional due to potential side effects.
A physical therapist can offer exercises and stretches tailored to strengthen the muscles and increase flexibility, thereby promoting healing and preventing further injury.
- Eccentric Exercises:
These exercises, in which the muscle lengthens under load, can be especially effective in treating tendinopathies, including quadriceps tendonitis.
- Corticosteroid Injections:
For cases where pain and inflammation are severe and persistent, corticosteroid injections can be considered. They offer temporary relief, but repeated injections may weaken the tendon and are not always recommended.
- Platelet-rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy:
PRP involves drawing a small amount of the patient’s blood, processing it to increase the concentration of platelets, and then injecting it into the injured tendon. This can promote healing, although research on its efficacy is still ongoing.
- Surgical Intervention:
In rare cases where the tendon is severely damaged or if other treatments fail, surgery might be considered. This can involve cleaning and repairing the damaged tendon.
- Supportive Devices:
Knee braces or straps can sometimes be used to offload the tendon, reduce strain, and provide support during the healing phase.
- Alternative Therapies:
Some patients seek out acupuncture, laser therapy, or shockwave therapy as potential treatments. While there’s varying evidence of their efficacy for quadriceps tendonitis, some individuals report relief.
What Are The Immediate First-Aid Measures?
There are immediate first-aid measures that can be taken to reduce pain, swelling, and further injury. These measures are encapsulated in the acronym R.I.C.E:
Rest
- Significance: Ceasing activity reduces the risk of aggravating the injury and allows the body to start the healing process.
- Action: Stop the activity that caused or intensified the pain immediately. Refrain from putting unnecessary strain on the injured area for at least the next 24-48 hours.
Ice
Significance: Cold application helps constrict blood vessels, reducing inflammation and numbing the area to diminish pain.
Action:
- Use cold packs, crushed ice in a plastic bag, or even a bag of frozen peas wrapped in a cloth or towel.
- Apply the cold source to the injured area for 20 minutes at a time.
- Wait at least an hour between ice applications to avoid cold-induced injuries.
- Continue this process for the first 48 hours post-injury.
Compression
Significance: Applying pressure helps to limit swelling and provides support to the injured area.
Action:
- Use an elastic bandage or compression wrap, starting from a point just below the injury site and moving upwards.
- Ensure the wrap is snug but not too tight. If you notice tingling, numbness, increased pain, or the area becomes pale or blue, loosen the bandage—it’s too tight.
Elevation
Significance: Raising the injured area helps reduce swelling by allowing fluids to drain away from the site due to gravity.
Action:
- Prop up the injured leg on pillows or cushions, ensuring it’s above the level of the heart.
- Aim to maintain this elevated position as much as possible during the first 24-48 hours after the injury.
Avoid Heat, Alcohol, and Massage
Significance: In the initial stages post-injury, these can increase blood flow to the area, potentially worsening swelling and pain.
Action:
- Do not apply heat packs or take hot baths for the first 48 hours.
- Avoid consuming alcohol as it can exacerbate inflammation.
- Refrain from massaging the injured area, as it may intensify the injury or increase swelling.
Note the Severity and Symptoms
- Significance: Understanding the severity and nature of the injury can help medical professionals provide the best care when consulted.
- Action: Make a mental or written note of how the injury occurred, the type and location of pain, the presence of any swelling or bruising, and any other unusual symptoms.
Are Surgical Interventions Needed?
 For most cases of quadriceps tendonitis, treatments are effective and surgery is not required. However, surgical intervention might be considered in certain circumstances:
For most cases of quadriceps tendonitis, treatments are effective and surgery is not required. However, surgical intervention might be considered in certain circumstances:
- Chronic Quadriceps Tendonitis: If the condition persists and doesn’t respond to non-surgical treatments over an extended period, surgery might be contemplated to address any degenerative changes or significant damage to the tendon.
- Tendon Rupture: A complete rupture or tear of the quadriceps tendon is a more severe injury and usually requires surgical repair. In these cases, the tendon has separated from the kneecap (or has a significant tear), and surgical intervention becomes necessary to reattach or repair the tendon.
- Presence of Calcifications: Sometimes, chronic tendonitis can lead to the formation of calcifications within the tendon. If these are causing symptoms and not responding to other treatments, surgical removal might be considered.
- Failed Conservative Treatments: If all non-surgical treatments like physical therapy, medications, rest, and other interventions fail to provide relief after an extended period, surgery may be an option to consider.
- Severe Pain and Disability: In rare cases, if the pain is so severe that it severely impacts daily activities and quality of life. And if other treatments aren’t effective, then surgery might be suggested.
How Can I Prevent Quadriceps Tendonitis?
Preventing quadriceps tendonitis is crucial, especially for those who are at a higher risk due to their physical activities or past injuries. Here are some strategies that can help prevent or reduce the risk of developing this condition:
- Warm-Up Properly
Engage in dynamic stretches and light aerobic exercises like jogging or cycling before participating in more intense activities.
- Regular Strength Training
Focusing on the quadriceps, hamstrings, and calf muscles can help in supporting the knee. Eccentric exercises, which involve muscle lengthening under load, can be particularly beneficial for tendon health.
- Maintain Flexibility
Incorporate stretching exercises into your routine, emphasizing the quadriceps, hamstrings, and calf muscles.
- Gradual Increase in Activity
If starting a new exercise regimen or sport, it’s crucial to progress gradually. This approach allows the body to adapt to increased demands and reduces the risk of overuse injuries.
- Use Proper Footwear
Wear shoes that provide good support and fit well. For athletes and runners, it’s beneficial to replace shoes regularly and consider orthotics if necessary.
- Modify Training Techniques
Ensure that your form and technique are correct in any physical activity. This can reduce unnecessary strain on the knees.
- Cross-Training
Engaging in a variety of exercises can help to avoid the overuse of specific muscles and tendons. For instance, if you’re a runner, mix in some cycling or swimming.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight
Carrying extra weight can increase stress on the knees. By maintaining a healthy weight, you can reduce the risk of various knee-related issues, including quadriceps tendonitis.
- Listen to Your Body
If you start experiencing pain or discomfort, don’t push through it. Rest, apply the R.I.C.E. method, and consult a healthcare professional if needed.
- Stay Hydrated
Proper hydration can aid in muscle function and reduce the risk of cramps and strains.
Is Massage Good For Quad Tendonitis?
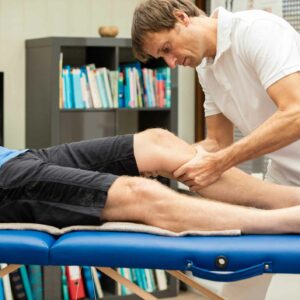 Massage therapy can offer several benefits for those suffering from quadriceps tendonitis. By increasing blood flow to the affected area, massage can enhance the delivery of essential nutrients required for healing while also promoting muscle relaxation. This relaxation can reduce pain, and improve flexibility. Furthermore, certain massage techniques may assist in breaking down scar tissue associated with chronic tendonitis.
Massage therapy can offer several benefits for those suffering from quadriceps tendonitis. By increasing blood flow to the affected area, massage can enhance the delivery of essential nutrients required for healing while also promoting muscle relaxation. This relaxation can reduce pain, and improve flexibility. Furthermore, certain massage techniques may assist in breaking down scar tissue associated with chronic tendonitis.
However, it’s vital to approach massage with caution. Aggressive massage, especially during the acute phase of injury (first 48-72 hours), can exacerbate inflammation. It’s recommended to seek the services of a licensed massage therapist or physical therapist familiar with treating tendonitis. They can apply appropriate techniques tailored to the individual’s condition and needs. Always consult with a healthcare provider before initiating any new treatment.
Conclusion
In addressing quadriceps tendonitis, a comprehensive understanding of its causes, treatment options, and preventive measures is essential. While immediate first-aid responses lay the groundwork for recovery, longer-term treatments, from physical therapy to potential surgical interventions, can play a decisive role based on the severity. Prevention, integrating measures like proper warm-ups, strength training, and maintaining flexibility, remains a cornerstone in avoiding recurrent episodes.
It’s paramount, however, always to seek professional guidance and be attuned to one’s body, ensuring that any treatment or preventive measure adopted aligns with individual needs and health conditions. If you’re experiencing Knee pain, physical therapy for knee pain at PhysioMantra can help: Book an online physical therapy session.



