Knee bursitis, a common ailment among individuals of varying lifestyles, can be both a painful and frustrating experience. This condition, characterized by the inflammation of the bursae – small sacs filled with fluid that cushion your joints – can significantly impact your mobility and quality of life. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the intricacies of knee bursitis, exploring its causes, symptoms, treatment options, prevention techniques, and more.
Contents
Understanding Knee Bursitis: Causes and Symptoms
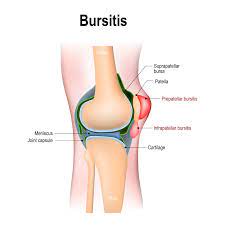
Knee bursitis, also known as prepatellar bursitis or “housemaid’s knee,” is a condition characterized by inflammation of one or more bursae around the knee joint. Bursae are small, fluid-filled sacs that act as cushions between bones, tendons, muscles, and skin, reducing friction and allowing smooth movement. When these bursae become irritated or inflamed, it can lead to knee bursitis
Common Causes of Knee Bursitis
Knee bursitis can be caused by a variety of factors, often related to excessive pressure, friction, or inflammation around the knee joint. Here are some common causes of knee bursitis:
- Repetitive Kneeling or Pressure: Prolonged or repetitive kneeling on hard surfaces, without proper knee protection, can put excessive pressure on the bursae around the kneecap. This can lead to irritation and inflammation of the bursa, causing knee bursitis. Jobs or activities that require frequent kneeling, such as gardening, construction work, or cleaning, can contribute to this.
- Direct Trauma or Impact: A sudden blow, fall, or direct impact to the front of the knee can cause the bursa to become inflamed. This can occur in contact sports, accidents, or falls where the knee hits a hard surface.
- Overuse or Excessive Activity: Engaging in activities that involve repetitive or excessive movements of the knee joint, such as running, jumping, or cycling, can lead to overuse and irritation of the bursa, potentially resulting in bursitis.
- Infection: In some cases, knee bursitis can be caused by a bacterial infection in the bursa. This is less common but can occur if bacteria enter the bursa through an open wound or due to a compromised immune system. Infected bursitis often causes more severe symptoms and may require prompt medical attention.
- Gout: Gout is a type of arthritis caused by the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints. It can also affect bursae, leading to inflammation and bursitis in the knee
Recognizing Symptoms of Knee Bursitis
Recognizing the symptoms of knee bursitis is important for early diagnosis and appropriate treatment. The symptoms can vary in intensity and may come on gradually or suddenly. Here’s what to look out for:
- Swelling: One of the hallmark symptoms of knee bursitis is swelling around the front of the knee. The affected area may appear visibly swollen and feel puffy to the touch.
- Pain: You may experience pain localized around the front of the knee, where the bursa is inflamed. The pain can range from mild discomfort to more severe and sharp pain. It might worsen when pressure is applied to the knee or during movements that involve bending or extending the knee.
- Redness and Warmth: Inflammation can cause the skin over the affected bursa to become red and warm to the touch. This is particularly noticeable if there is an infection associated with the bursitis.
- Limited Range of Motion: Swelling and pain can limit your ability to fully bend or extend your knee. You might feel stiffness and resistance when trying to move the joint.
- Tenderness: The area over the inflamed bursa may feel tender when you press on it. This tenderness might extend beyond the swollen area.
- Pain with Activity: Activities that involve bending the knee, such as walking, climbing stairs, or squatting, might exacerbate the pain and discomfort.
- Pain at Rest: In some cases, the pain might persist even when you’re not engaging in any activities. It can be present when you’re sitting or lying down.
Diagnosis: Identifying Knee Bursitis
Diagnosing knee bursitis typically involves a combination of a thorough medical history, physical examination, and, in some cases, medical imaging. Here’s how the diagnosis process for knee bursitis usually unfolds:
- Medical History: Your doctor will begin by asking about your symptoms, the onset and duration of pain, any triggering activities or injuries, and any previous medical conditions that might be relevant. Providing information about your daily activities, occupation, and any recent changes can help in identifying potential causes.
- Physical Examination: Your doctor will examine your knee, looking for signs of swelling, redness, warmth, and tenderness. They may also assess your range of motion and conduct specific tests to help differentiate knee bursitis from other knee-related conditions.
- Palpation: The doctor will gently press and feel around the area of the knee to identify the location of tenderness and swelling. This helps determine which bursa is likely affected.
- Range of Motion Testing: Your doctor may ask you to move your knee in various directions to assess your range of motion and identify any limitations or pain points.
- Imaging: In some cases, imaging tests such as X-rays or MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) may be ordered. X-rays can help rule out other structural issues, while an MRI provides detailed images of the soft tissues, including the bursae, helping to confirm the diagnosis and assess the extent of inflammation.
Treatment Options for Knee Bursitis
The treatment approach for knee bursitis depends on the underlying cause, severity of symptoms, and individual factors. In many cases, knee bursitis can be effectively managed with conservative treatments. Here are some common treatment options:
- Rest and Activity Modification: Resting the affected knee and avoiding activities that exacerbate the symptoms is a crucial first step in the treatment process. This allows the inflamed bursa to heal. If the bursitis was caused by repetitive kneeling or overuse, modifying or avoiding those activities is important.
- Ice and Heat Therapy: Applying ice packs to the affected area for 15-20 minutes at a time can help reduce swelling and alleviate pain. Heat therapy, such as warm compresses, can also be beneficial for soothing discomfort.
- Pain Medications: Over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen or naproxen can help reduce pain, inflammation, and swelling. Always follow the recommended dosages and consult a healthcare professional before using these medications.
- Physical Therapy: A physical therapist can guide you through exercises that help improve the range of motion, strength, and flexibility of the knee joint. They can also provide techniques to reduce inflammation and pain.
- Corticosteroid Injections: In some cases, your doctor may recommend a corticosteroid injection into the inflamed bursa. These injections can provide rapid relief by reducing inflammation. However, they are usually reserved for cases that do not respond to more conservative treatments.
Preventing Knee Bursitis: Tips and Techniques

Preventing knee bursitis involves making certain lifestyle adjustments and adopting practices that reduce the risk of excessive pressure, friction, and inflammation around the knee joint. Here are some tips and techniques to help prevent knee bursitis:
- Use Proper Knee Protection: If your activities involve kneeling or putting pressure on your knees, such as gardening or construction work, use knee pads or cushions to reduce direct pressure on the knee joint.
- Maintain Proper Posture: When kneeling, squatting, or lifting, maintain proper body mechanics to avoid unnecessary strain on your knees. Use your leg muscles and avoid excessive bending or twisting.
- Take Breaks: If your job or hobby involves prolonged kneeling or repetitive motions, take frequent breaks to give your knees a chance to rest and recover.
- Use Proper Footwear: Wear shoes that provide adequate support and cushioning, especially if you are engaged in activities that require a lot of walking or standing.
- Weight Management: Maintain a healthy weight to reduce excess stress on your knees. Excess body weight can contribute to knee problems, including bursitis.
- Stretching and Strengthening: Incorporate regular stretching and strengthening exercises for the muscles around your knees. Strong and flexible muscles can help support your knee joint and reduce the risk of overuse injuries.
- Warm-Up and Cool Down: Before engaging in physical activities, warm up your muscles with gentle exercises and stretches. Afterward, cool down with more stretches to prevent stiffness and tension.
When Surgery Is Necessary
Surgical Options for Severe Cases
While most cases of knee bursitis can be effectively managed through conservative treatments, surgical intervention may be necessary for severe and persistent cases. Surgical procedures aim to remove the inflamed bursa and address underlying issues.
Recovery and Rehabilitation After Surgery
Recovering from knee bursitis surgery involves a carefully structured rehabilitation program. Physical therapy and gradual reintroduction of activities are crucial for regaining strength and mobility.
Coping with Knee Bursitis: Mental and Emotional Well-being
Dealing with knee bursitis not only involves physical aspects but also has an impact on your mental and emotional well-being. Coping effectively with knee bursitis can help you manage the challenges and maintain a positive outlook during your recovery. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Stay Informed: Understanding your condition and the recovery process can help alleviate anxiety. Ask your healthcare provider questions about your treatment plan, expected recovery time, and what you can do to aid healing.
- Practice Patience: Recovery from knee bursitis takes time. Be patient with yourself and your body as you navigate the healing process.
- Set Realistic Expectations: Understand that progress might be gradual. Set achievable goals and celebrate even small improvements.
- Seek Support: Don’t hesitate to lean on friends, family, and loved ones for emotional support. Share your concerns and feelings with them, as having a strong support network can make a significant difference.
- Engage in Relaxation Techniques: Practices like deep breathing, meditation, and mindfulness can help reduce stress and anxiety. These techniques can be beneficial for managing any discomfort and promoting relaxation.
Conclusion
Knee bursitis may present challenges, but with the right approach and dedication, managing and recovering from it is entirely achievable. By implementing effective treatment strategies, seeking expert advice, and maintaining a positive mindset, you can regain comfort and mobility in your daily life.
If you’re experiencing Knee pain, physical therapy for knee pain at PhysioMantra can help: Book an online physical therapy session.



