Knee problems are a common issue that can affect people of all ages and walks of life. Whether you’re an athlete, a desk worker, or a retiree, your knees play a crucial role in your daily activities and mobility. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the world of knee problems, exploring their causes, preventive measures, and effective management strategies to keep your knees healthy and pain-free.
Contents
Common Types Of Knee Problems
The knee joint, a complex hinge joint, plays a pivotal role in our daily activities, allowing us to walk, run, jump, and perform a multitude of movements. However, this remarkable joint is susceptible to a range of issues that can cause pain, discomfort, and reduced mobility. To effectively address knee problems, it’s essential to understand their causes, types, and how they impact our lives.
Types of Knee Problems:
- Osteoarthritis: This is the most prevalent form of arthritis that affects the knee joint. Osteoarthritis occurs when the protective cartilage that cushions the ends of bones gradually deteriorates, leading to pain, stiffness, and decreased joint flexibility.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: Unlike osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the synovium, the lining of the membranes that surround the knee joint. This leads to inflammation, pain, and joint damage.
- Meniscus Tears: The meniscus is a rubbery, C-shaped disc that acts as a cushion between your shinbone and thighbone. Tears in the meniscus can occur due to sudden twisting or traumatic injuries, causing pain and limited knee function.
- Ligament Injuries: Injuries to knee ligaments, such as the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) or posterior cruciate ligament (PCL), can result from sports accidents or sudden movements. These injuries often lead to instability and pain.
- Tendonitis: Tendonitis involves inflammation of the tendons around the knee joint, often due to repetitive movements or overuse. It can lead to pain during activities that involve bending or extending the knee.
- Bursitis: Bursitis occurs when the bursae, fluid-filled sacs that cushion the knee joint, become inflamed. This can result in swelling, tenderness, and pain.
- Chondromalacia Patellae: This condition involves the softening and breakdown of the cartilage on the underside of the kneecap (patella). It often causes pain, particularly when climbing stairs or kneeling.
Effective Treatment Options For Knee Problems
Knee problems can vary widely in severity and cause, and treatment options depend on the specific diagnosis and individual factors. Here’s an overview of common treatment options for knee problems:
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen may help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation. For more severe pain, your healthcare provider may prescribe stronger medications.
- Injections: Corticosteroid injections can be used to reduce inflammation and relieve pain in cases of conditions like osteoarthritis. Hyaluronic acid injections provide lubrication to the knee joint for improved mobility.
- Bracing and Supports: Depending on the issue, wearing a knee brace or support can provide stability and relieve pain. Custom orthotics or shoe inserts may also be recommended.
- RICE Protocol: Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation (RICE) can be effective for managing acute knee injuries. This approach helps reduce swelling, alleviate pain, and promote healing.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for reducing stress on the knee joint, especially in cases of osteoarthritis.
- Surgery: In more severe cases, surgery may be necessary. Common surgical interventions for knee problems include arthroscopy (minimally invasive), ligament reconstruction, meniscus repair, and joint replacement (knee arthroplasty).
- Arthroscopy: This minimally invasive procedure involves inserting a tiny camera and instruments into the knee joint to diagnose and treat various issues, such as removing damaged tissue or repairing ligaments.
- Ligament Reconstruction: Surgery may be required to reconstruct a torn ligament, using grafts from other body parts or from a donor.
- Joint Replacement: Total knee replacement surgery involves replacing the damaged knee joint with an artificial one.
- Regenerative Medicine: Emerging treatments like platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and stem cell therapy are being explored for their potential to promote healing and reduce pain in knee problems.
- Complementary Therapies: Some individuals find relief from knee pain through complementary therapies like acupuncture or chiropractic care.
Benefits Of Physical Therapy In Relieving Knee Pain
Here are some key advantages of undergoing physical therapy for knee issues:
- Pain Reduction: Physical therapists use various techniques, including manual therapy, modalities like heat and ice, and targeted exercises, to reduce pain and discomfort associated with knee problems.
- Improved Function: Physical therapy aims to enhance the overall function of your knee joint. Through exercises that focus on strengthening muscles, improving range of motion, and promoting better joint mechanics, you can regain better mobility and function.
- Avoiding Surgery: In many cases, physical therapy can help individuals avoid the need for surgery. By addressing knee problems early and effectively, you may prevent the progression of your condition to a point where surgery becomes necessary.
- Faster Recovery: For those who have undergone knee surgery, physical therapy plays a critical role in the recovery process. It helps restore normal function and mobility in the shortest time possible.
- Prevent Recurrence: Physical therapy not only addresses current knee problems but also focuses on preventing future issues. By strengthening the muscles around the knee, improving joint mechanics, and providing education on proper movement and posture, PT can reduce the risk of recurrence.
- Non-Invasive Approach: Physical therapy is a non-invasive and drug-free approach to managing knee problems, making it a safe and natural choice for many individuals.
- Enhanced Quality of Life: By reducing pain, improving function, and preventing future issues, physical therapy can significantly enhance your overall quality of life. You’ll be able to engage in activities you enjoy without the limitations of knee pain.
- Cost-Effective: In many cases, physical therapy is a cost-effective alternative to surgery or long-term medication use, making it an economical choice for managing knee problems.
- Functional Independence: Physical therapy empowers individuals to regain their functional independence, enabling them to perform daily activities with ease and confidence.
Exercises To Help Deal With Knee Problems
Exercising the right way can help relieve knee pain and improve the strength and flexibility of the muscles around the knee joint. However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider or physical therapist before starting any exercise program, especially if you have a knee condition. Here are some exercises that may be beneficial for relieving knee pain:
Quadriceps Sets
- Lay down on the floor with your legs extended.
- Tighten the quadriceps muscles on the front of your thigh by pressing the back of your knee into the floor.
- Hold for a few seconds, then relax.
- Repeat for several sets, gradually increasing the hold time.
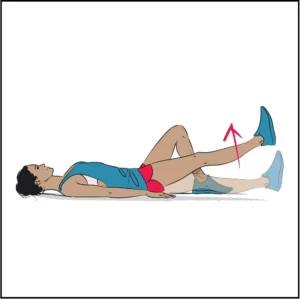
Straight Leg Raises
- Lie on your back with one leg straight and the other bent.
- Lift the straight leg a few inches off the ground, keeping your knee extended.
- Hold for a few seconds and then lower it.
- Repeat with the other leg.
- Perform several sets on each leg.
Hamstring Curls
- Stand near a stable surface, like a chair or countertop, for support.
- Bend one knee and bring your heel toward your buttocks.
- Hold for a few seconds and then lower your foot.
- Repeat on the other leg.
- Do several sets on each leg.
Step-Ups
- Use a stable step or platform.
- Step up onto the platform with one foot, then bring the other foot up.
- Step down with the first foot, followed by the second.
- Repeat this pattern for several sets, alternating the leading foot.
Leg Press
- If you have access to a leg press machine, it can be beneficial for strengthening the quadriceps.
- Follow the instructions provided by the machine and start with a comfortable weight.
Seated Marching
- Sit on a chair with your feet flat on the floor.
- Lift one knee as high as you can while keeping your foot on the ground.
- Lower it and repeat with the other leg.
- Perform several sets of seated marches.
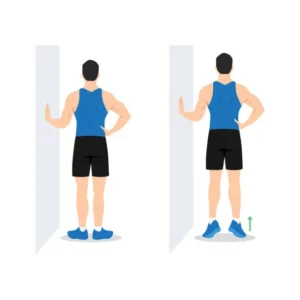
Calf Raises
- Stand with your feet hip-width apart, near a wall, or sturdy support for balance.
- Rise up onto your toes and then lower your heels back down.
- Repeat for several sets to strengthen your calf muscles, which indirectly support the knee joint
Remember to start slowly, use proper form, and increase the intensity and duration of exercises gradually. If you experience increased pain or discomfort during any exercise, stop immediately and consult with a healthcare provider or physical therapist.
Conclusion
In conclusion, knee problems can be challenging, but they are not invincible. With the right knowledge, guidance, and commitment, you can take significant steps toward maintaining or reclaiming the health of your knees. Whether you’re dealing with an injury, or chronic condition, or seeking preventive measures, understanding the causes, seeking appropriate treatment, and adopting a proactive approach to knee care can make a substantial difference in your quality of life.
Remember, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider or orthopedic specialist to accurately diagnose and address your knee issues.
If you’re experiencing Knee pain, physical therapy for knee pain at PhysioMantra can help: Book an online physical therapy session.