In the hustle and bustle of our modern lives, we often neglect the signals our bodies send us. One such alarming message comes in the form of lower back and knee pain. These twin discomforts are remarkably common, affecting millions worldwide. But fear not, for in this article, we’ll navigate the intricacies of these pains and explore effective ways to bid them farewell.
Contents
Understanding the Connection between Lower Back and Knee Pain

Lower back and knee pain can often be interconnected due to the complex nature of the musculoskeletal system. The spine, hips, and knees are all part of a biomechanical chain, and issues in one area can lead to problems in another. Here’s how the connection between lower back and knee pain works:
- Biomechanical Chain: The body is a series of interconnected joints and muscles that work together to facilitate movement. The lower back, hips, knees, and ankles are all part of this chain. Dysfunction in one part of the chain can affect the others.
- Muscle Imbalances: Imbalances in muscle strength and flexibility can lead to compensations. For example, if the muscles in your hips or lower back are weak or tight, your body might alter its movement patterns, potentially putting additional stress on your knees. Over time, this can lead to pain and discomfort in both areas.
- Posture and Alignment: Poor posture or alignment can contribute to both lower back and knee pain. If you have a habit of slouching or standing in an improper alignment, it can lead to increased pressure on your lower back and knees, causing pain in both areas.
- Nerve Irritation: The nerves that supply the lower back also travel down the legs and provide sensation to the knees. Irritation or compression of these nerves in the lower back can lead to pain that radiates down into the knees, mimicking knee pain.
Causes of Lower Back and Knee Pain
Lower back and knee pain can be caused by a variety of factors, ranging from acute injuries to chronic conditions. Here are some common causes of lower back and knee pain:
1. Muscle Strains and Sprains: Overstretching or tearing of muscles or ligaments in the lower back or around the knee joint can lead to pain. These injuries often result from sudden movements or overexertion.
2. Herniated Disc: A herniated disc occurs when the soft inner portion of a spinal disc pushes through the outer layer. This can put pressure on nearby nerves, causing lower back pain that may also radiate down the leg, mimicking knee pain.
3. Osteoarthritis: This is a degenerative joint disease that occurs when the protective cartilage between bones wears down over time. It can affect both the lower back and knee joints, causing pain, stiffness, and reduced range of motion.
4. Sciatica: Sciatica is a condition where the sciatic nerve, which runs from the lower back down the legs, becomes compressed or irritated. This can lead to pain that starts in the lower back and radiates down the back of the leg, often reaching the knee.
5. Disc Degeneration: As the spinal discs naturally wear down with age, it can lead to decreased disc height and changes in spinal alignment. This can contribute to lower back pain and impact the way weight is distributed to the knees.
6. Spondylolisthesis: This occurs when one vertebra slips forward over the vertebra below it. It can cause lower back pain and potentially affect the alignment and stability of the spine, which may indirectly impact the knees.
7. Poor Posture: Bad posture, such as slouching or sitting for extended periods without proper support, can strain the muscles and ligaments in the lower back and knees, leading to pain.
8. Overuse or Repetitive Strain: Activities that involve repetitive movements, especially if they are performed with poor form, can lead to overuse injuries in both the lower back and knees.
9. Obesity: Excess weight can put additional stress on both the lower back and knee joints, increasing the risk of pain and joint problems.
10. Gait Abnormalities: An abnormal walking pattern can affect the distribution of forces through the lower back and knees, leading to pain in both areas.
Symptoms of Lower Back and Knee Pain

Lower back and knee pain can present with a range of symptoms, which can vary depending on the underlying cause of the pain. Here are some common symptoms associated with lower back and knee pain:
Symptoms of Lower Back Pain:
- Localized Pain: Pain that is primarily concentrated in the lower back region, often ranging from a dull ache to a sharp, stabbing sensation.
- Pain Radiation: Pain that radiates from the lower back down into the buttocks, hips, and possibly even into the legs. This is also a sign in conditions like sciatica or herniated discs.
- Stiffness: Feeling of stiffness and reduced flexibility in the lower back, especially after periods of inactivity or rest.
- Muscle Spasms: Involuntary muscle contractions in the lower back that can be painful and cause temporary immobility.
- Pain with Movement: Pain that worsens with certain movements, such as bending forward, lifting, twisting, or standing for extended periods.
- Numbness or Tingling: Sensations of numbness, tingling, or “pins and needles” in the lower back or down the legs, particularly if nerve involvement is present.
- Weakness: Reduced strength in the muscles of the lower back, hips, or legs, making it difficult to perform certain activities.
Symptoms of Knee Pain:
- Pain Location: Pain located around the knee joint, which can vary in intensity from mild discomfort to severe pain.
- Swelling: Swelling or inflammation around the knee joint, often accompanied by warmth and redness.
- Stiffness: Feeling of stiffness or decreased range of motion in the knee joint, especially after periods of rest or inactivity.
- Clicking or Popping: Audible or palpable sensations of clicking, popping, or grinding within the knee joint during movement.
- Difficulty Bearing Weight: Pain and discomfort when putting weight on the affected knee, such as when standing, walking, or climbing stairs.
- Instability: Feeling of instability or a sensation that the knee is “giving way” during movement, which can be indicative of ligament or meniscus injuries.
- Locking: Sensation that the knee joint gets stuck or locked in a certain position, often caused by a meniscus tear or other structural issue.
- Pain with Activities: Pain that worsens with specific activities, such as squatting, running, or kneeling.
- Numbness or Tingling: Similar to lower back pain, numbness or tingling sensations can sometimes be there knee area if nerve involvement is present.
Diagnostic Tests for Lower Back and Knee Pain
When dealing with lower back and knee pain, healthcare professionals may use various diagnostic tests to accurately identify the underlying cause of the pain. The choice of tests will depend on the individual’s symptoms, medical history, and the suspected cause of the pain. Here are some common diagnostic tests for lower back and knee pain:
1. Physical Examination: A thorough physical examination by a healthcare provider is often the first step. They will assess your range of motion, muscle strength, and reflexes, and perform specific tests to pinpoint the source of pain and any associated issues.
2. Imaging Studies:
- X-rays: X-rays provide detailed images of bones. They can help identify fractures, bone degeneration, alignment issues, and other bony abnormalities.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): MRI uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create detailed images of soft tissues, such as muscles, ligaments, discs, and nerves. It’s useful for diagnosing herniated discs, nerve compression, and soft tissue injuries.
- CT Scan (Computed Tomography): CT scans provide detailed cross-sectional images of the body. They are often used to visualize bone structures and can be helpful in cases where an MRI may not be suitable.
3. Ultrasound: Ultrasound imaging uses sound waves to create real-time images of soft tissues. It’s commonly used to assess inflammation, joint effusion (fluid buildup), and certain soft tissue injuries.
Treatment Options
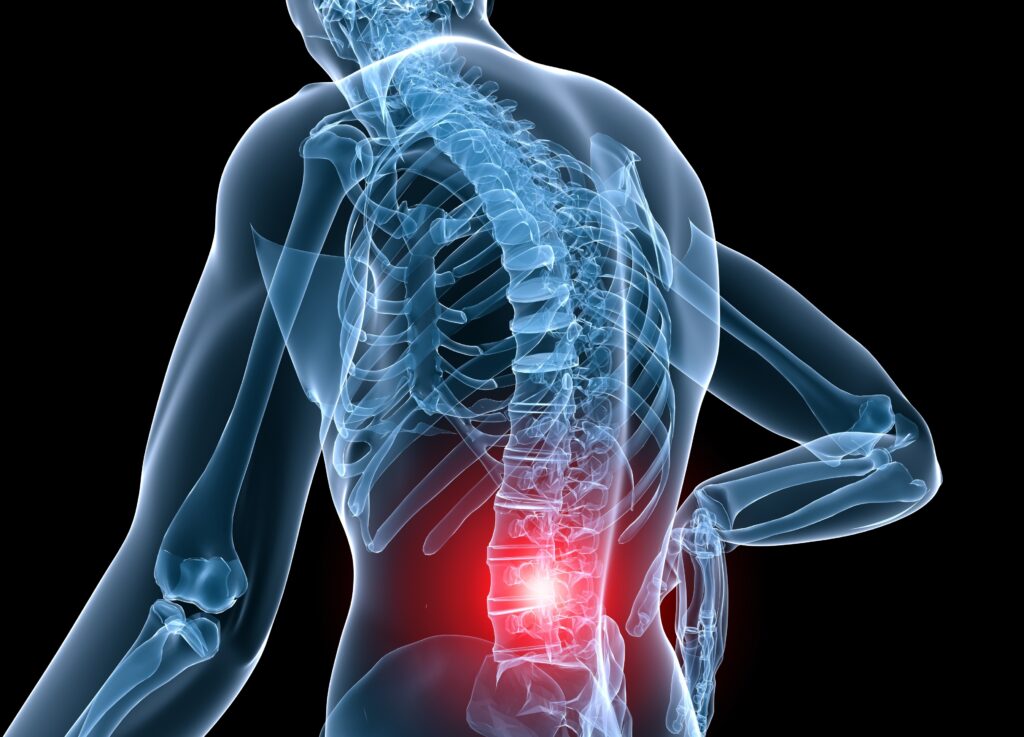
Addressing these pains involves a multi-pronged approach. Lifestyle changes can also help– maintaining a healthy weight, staying active, and practicing good posture are essential. Physical therapy, a cornerstone of non-invasive treatment, can work wonders. Medications, both over-the-counter and prescribed, offer temporary relief. Some other treatment options are:
Stretching and Strengthening Exercises
Exercise might seem counterintuitive when in pain, but the right movements can be transformative. Gentle stretches and targeted strengthening exercises can alleviate discomfort by enhancing flexibility and building muscle support. Think of it as retraining your body to move harmoniously.
Posture Correction and Ergonomics
Picture a puppeteer – the strings need to be pulled just right for the puppet to dance gracefully. Our body is the puppet, and good posture is the puppeteer’s skill. Poor posture places undue stress on our joints, contributing to pain. Practicing proper ergonomics at work and home can have a profound impact on pain reduction.
Alternative Therapies
Venturing beyond conventional treatments, alternative therapies have gained popularity. Acupuncture, with its ancient roots, targets energy pathways to alleviate pain. Chiropractic care seeks to align the body through spinal adjustments. While evidence varies, many swear by the relief these therapies provide.
Surgical Interventions
When all else fails, surgery might be considered. Advances in medical technology offer various surgical procedures to address both lower back and knee issues. From spinal fusion to knee replacement, these interventions aim to restore functionality and alleviate pain.
Conclusion
Lower back and knee pain need not be unwelcome companions in your journey. By understanding the connection, making positive lifestyle changes, and exploring various treatment avenues, you can pave the way for a pain-free existence. Remember, your body is resilient, and with the right care, you can reclaim your vitality.
If you’re experiencing Knee pain, physical therapy for knee pain at PhysioMantra can help: Book an online physical therapy session.