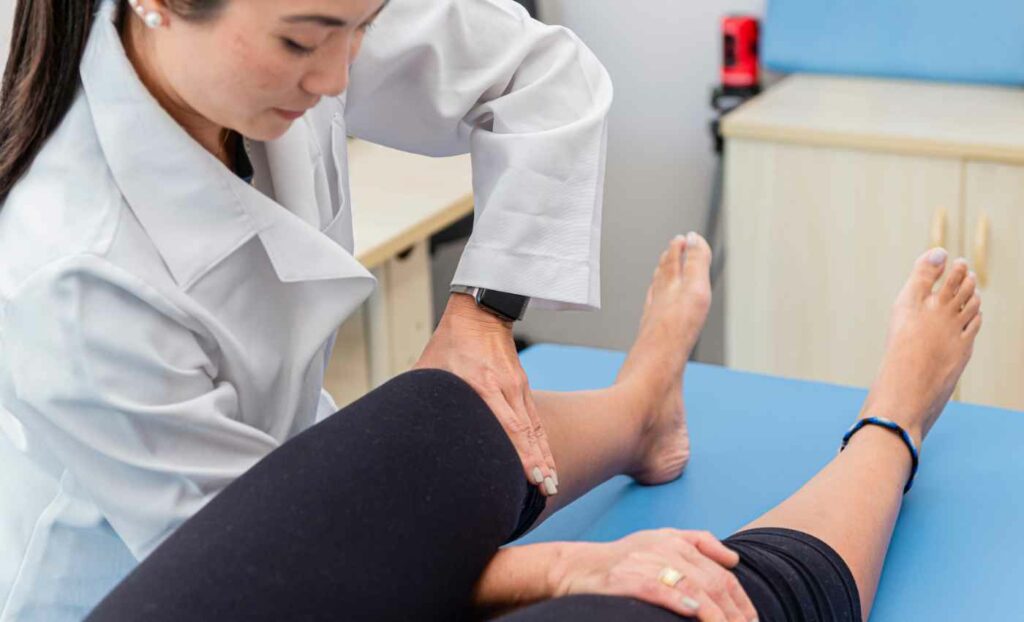
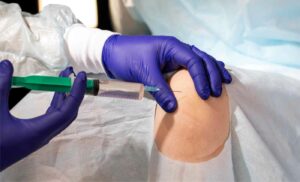
Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome (PFPS) is a common orthopedic condition that can affect individuals of all ages and activity levels. It is mainly characterized by pain around the front of the knee, especially around or behind the kneecap (patella), PFPS can hinder daily activities and impact an individual’s quality of life. In this blog, we will delve into the causes, symptoms, and effective rehabilitation strategies for managing Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome. So, let’s dive in.
Contents
- 1 Understanding Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome
- 2 Potential Causes of Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome
- 3 Treatment For PFPS
- 3.1 Rest and Activity Modification
- 3.2 Pain Management
- 3.3 Physical Therapy
- 3.4 Biomechanical Assessment
- 3.5 Stretching and Flexibility Exercises
- 3.6 Taping and Bracing
- 3.7 Footwear Assessment
- 3.8 Activity Modification and Gradual Return to Exercise
- 3.9 Electromodalities
- 3.10 Patient Education
- 3.11 Injections
- 3.12 Surgical Consideration
- 4 Medical Treatments for Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome (PFPS)
- 5 How Long Does It Take To Recover From PFPS?
- 6 Lifestyle Changes for Managing PFPS
- 7 Conclusion
Understanding Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome%27%20fill-opacity%3D%27.5%27%3E%3Cellipse%20fill%3D%22%237b7785%22%20fill-opacity%3D%22.5%22%20rx%3D%221%22%20ry%3D%221%22%20transform%3D%22matrix(-39.6292%20-32.57084%2090.13478%20-109.66771%20264%2011.1)%22%2F%3E%3Cellipse%20fill%3D%22%23faf9f4%22%20fill-opacity%3D%22.5%22%20rx%3D%221%22%20ry%3D%221%22%20transform%3D%22matrix(-10.86188%20-144.45835%2061.01456%20-4.5877%2086.9%2050.8)%22%2F%3E%3Cellipse%20fill%3D%22%23647de7%22%20fill-opacity%3D%22.5%22%20rx%3D%221%22%20ry%3D%221%22%20transform%3D%22rotate(98.7%2025.9%20160.4)%20scale(46.59157%2028.2961)%22%2F%3E%3Cellipse%20fill%3D%22%23f0efe9%22%20fill-opacity%3D%22.5%22%20rx%3D%221%22%20ry%3D%221%22%20transform%3D%22rotate(-31.7%20433.5%20-446.2)%20scale(44.08392%20104.29042)%22%2F%3E%3C%2Fg%3E%3C%2Fsvg%3E)
Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome (PFPS) commonly leads to a range of different symptoms that can vary in severity and frequency. Understanding these symptoms is important for an accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. Some symptoms of PFPS include:
Symptoms:
Knee Pain: The major symptom of PFPS is pain around or behind the kneecap. This pain is often a dull ache or a sharp, localized discomfort. The pain may worsen during activities that involve a lot of knee movement, for example, walking, running, jumping, squatting, or going up or down stairs.
Swelling and Tenderness: Swelling around the knee joint and tenderness when pressing on the kneecap or its surrounding structures is a pretty common symptoms of PFPS.
Discomfort with Prolonged Sitting: Sitting for long durations can worsen this. People with PFPS may find it uncomfortable to sit for long periods in positions such as during car rides, movie theater visits, or while doing some desk work.
Crepitus and Grinding Sensation: Some individuals with PFPS may also experience a sensation of grinding, popping, or crepitus in the knee joint when moving the knee. This is often caused by the movement of the kneecap over the femur.
Change in Movement Patterns: To relieve themselves of discomfort, people who have PFPS may unintentionally change their movement patterns. This can lead to changes in gait, alignment of the knees, and muscle activation, further adding to pain and dysfunction.
Symptoms in Both Knees: While PFPS typically affects one knee, it’s not uncommon for individuals to experience discomfort in both their knees, especially if there are underlying muscle imbalances or movement patterns.
Stiffness and Reduced Range of Motion: Some individuals experience stiffness in the knee joint and this may lead to a reduced range of motion. This can make activities that require bending or straightening the knee difficult.
Potential Causes of Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome
PFPS can arise from various factors affecting the kneecap and its surrounding structures. Although its exact cause may vary from one person to the other, there are several common factors and risk factors that contribute to the development of PFPS.
Poor Alignment: Misalignment of the kneecap (patella), can lead to uneven pressure and irritation, thus contributing to PFPS. Problems such as patellar tracking dysfunction, muscle imbalances, or altered movement patterns can cause improper kneecap alignment during movement.
Weakness and Muscle Imbalances: Muscle imbalances around the hip, thigh, and knee can contribute to PFPS. Weakness or poor coordination of muscles that stabilize the kneecap, such as the quadriceps and hip abductors, can lead to altered movement patterns and increased stress on the joint.
Inadequate Footwear: Wearing improper footwear, especially during physical activities, can impact the way the foot strikes the ground and the forces transmitted to the knee joint. Insufficient cushioning or lack of arch support can contribute to PFPS.
Previous Injuries: A history of knee injuries or trauma, such as sprains or fractures, can alter joint mechanics and increase the likelihood of developing PFPS. Improper healing or compensation strategies post-injury can contribute to ongoing knee pain.
Structural Factors: Certain structural factors can predispose individuals to PFPS. These include high arches, flat feet, or anatomical variations in the shape of the patella or femur that affect joint mechanics.
Treatment For PFPS
Effective treatment for PFPS involves an all-around approach that aims to reduce pain, address underlying causes, and promote long-term recovery. Here are some of the treatment options for PFPS:
Rest and Activity Modification
Resting the knee and avoiding intense activities that worsen the pain is the first step. Adjusting activities, like reducing high-impact exercises or avoiding prolonged sitting, can help individuals alleviate stress on the knee joints.
Pain Management
Over-the-counter pain medications and anti-inflammatory drugs can help manage pain and reduce inflammation. However, your healthcare provider usually recommends these in addition to other treatments.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy plays a very crucial role in PFPS treatment. In this, a physical therapist designs a specialized exercise program that focuses on muscle strengthening, flexibility, and biomechanical corrections. Strengthening the quadriceps, hip muscles, and core can really help stabilize the knee and alleviate pain.
Biomechanical Assessment
Physical therapists analyze movement patterns to be able to identify any biomechanical issues that might be contributing to PFPS. Addressing issues such as improper tracking of the patella can help realign the joint and reduce pain.
Stretching and Flexibility Exercises
Tight muscles around the hip, thigh, and knee can contribute to PFPS. Stretching exercises for muscles like the quadriceps, hamstrings, and iliotibial (IT) band help improve flexibility and reduce tension.
Taping and Bracing
Taping techniques and knee braces can provide support to the patellofemoral joint, helping to reduce pain and stabilize the kneecap during movement.
Footwear Assessment
Wearing appropriate footwear that provides proper arch support and cushioning is important for individuals with PFPS. In some cases, your doctor may recommend custom orthotics to provide additional support.
Activity Modification and Gradual Return to Exercise
After the initial pain subsides, a physical therapist guides the individual through a gradual return to activities and exercises. This progressive approach minimizes the risk of exacerbating the condition.
Electromodalities
Therapeutic modalities such as ultrasound, electrical stimulation, and ice can reduce pain and inflammation as part of a comprehensive treatment plan.
Patient Education
Educating individuals about PFPS, its causes, and proper self-care techniques is crucial. Learning about posture, body mechanics, and ways to prevent recurrence empowers individuals to manage their condition effectively.
Injections
In some cases, corticosteroid injections may be considered to provide temporary relief from pain and inflammation. However, these are typically used cautiously and as part of a comprehensive treatment plan.
Surgical Consideration
Surgery is usually considered only if conservative treatments fail to provide relief. Surgical options may include procedures to realign the patella or address structural abnormalities contributing to PFPS.
Medical Treatments for Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome (PFPS)
When conservative approaches such as physical therapy and lifestyle modifications are insufficient in managing Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome (PFPS), medical interventions may be considered.
Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): NSAIDs are commonly used to manage pain and inflammation that comes with PFPS. They can help reduce discomfort, swelling, and inflammation in the patellar region.
Corticosteroid Injections: In some cases, corticosteroid injections may be given directly into the knee joint to provide temporary relief from pain and discomfort. These injections are typically used when other treatments haven’t really worked well.
Bracing and Taping: A medical professional may recommend wearing a knee brace or using taping techniques. This can provide additional support to the patellofemoral joint, alleviate pain, and improve alignment during physical activities.
Shockwave Therapy: Extracorporeal shockwave therapy involves delivering high-energy sound waves to the knee joint. This non-invasive treatment can stimulate healing and improve blood flow.
How Long Does It Take To Recover From PFPS?
Recovery time for Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome (PFPS) can vary based on several factors, such as the severity of the condition, individual factors, and the effectiveness of the chosen treatment approach.
For mild cases of PFPS, recovery may be achieved within a few weeks to a couple of months with appropriate self-care and rest. In these instances, focusing on reducing stress on the knee joint, and practicing gentle exercises to strengthen the surrounding muscles, can often lead to gradual improvement.
For more moderate to severe cases of PFPS, where the pain has been ongoing and affects daily activities, recovery may take longer. A comprehensive approach is necessary, involving a combination of treatments such as physical therapy, targeted exercises, and potential modifications to activities that aggravate the condition.
Remember that every person’s journey to recovery is different. In some cases, individuals with PFPS may find relief within a few months, while others may require six months to a year or more to achieve significant improvement.
Lifestyle Changes for Managing PFPS
Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome (PFPS) can be effectively managed through a combination of treatments. Lifestyle modifications play a key role in promoting healing, preventing recurrence, and improving overall well-being. Here are some changes that you can make in order to manage PFPS
Maintain a Healthy Body Weight: Excess weight can put additional stress on the knee joint, exacerbating PFPS. Maintaining a healthy body weight through balanced nutrition and regular exercise can help reduce strain on the patellofemoral joint.
Stay Active with Low-Impact Exercises: While high-impact exercises can worsen PFPS symptoms, low-impact activities like swimming, cycling, and walking can help maintain cardiovascular fitness without overloading the knees.
Proper Footwear: Wearing supportive and well-cushioned footwear is essential. Choose shoes that provide adequate arch support and shock absorption to reduce strain on the knees.
Warm-Up and Cool-Down: Prior to exercise, perform a gentle warm-up that includes dynamic stretches to prepare the muscles for activity. After exercise, engage in static stretches to maintain flexibility and prevent tightness.
Gradual Progression: When returning to physical activities, progress gradually. Avoid sudden increases in intensity or duration to prevent overloading the knees.
Modify Activities: Avoid activities that aggravate PFPS symptoms. For example, if squatting or stair climbing is painful, find alternative exercises that don’t stress the knees.
Maintain Good Posture: Proper posture is crucial in preventing unnecessary strain on the knees. Be mindful of your body alignment during daily activities.
Incorporate Strength Training: Strengthening the muscles around the hip, thigh, and core helps provide better support to the knee joint. So, focus on exercises that target the hamstrings, and glutes.
Flexibility and Stretching: Regular stretching helps maintain flexibility and reduces muscle tightness.
Manage Stress: Chronic stress can contribute to muscle tension and affect pain perception. Incorporate stress-reducing techniques such as mindfulness, deep breathing, and relaxation exercises.
Conclusion
Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome can be a frustrating condition, but with the right approach, relief is attainable. A comprehensive treatment plan that includes physical therapy, targeted exercises, and lifestyle modifications can significantly improve knee function, reduce pain, and enhance the overall quality of life for individuals dealing with PFPS. If you’re experiencing knee pain, don’t hesitate to consult a medical professional or physical therapist for proper evaluation and guidance.
If you’re experiencing Knee pain, physical therapy for knee pain at PhysioMantra can help: Book an online physical therapy session.