The little-known Psoas Syndrome is a condition that is often overlooked and misdiagnosed. But it can drastically affect our quality of life. In this blog post, we aim to shed light on this elusive syndrome, its causes, symptoms, and most importantly, how to manage and overcome it. Let’s dive into the world of the psoas muscle, and discover how keeping it healthy can lead to a more pain-free and active life.
Contents
What Is Psoas Syndrome?
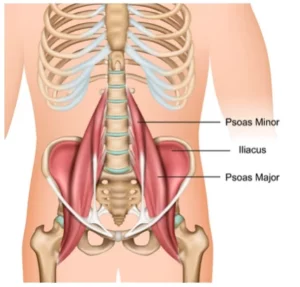 Psoas Syndrome is a relatively rare and often misdiagnosed condition that occurs when the psoas muscle – a large muscle located in the lumbar region of the spine that extends through the pelvis – is injured or strained. The psoas muscle is crucial for human movement and stability, connecting the upper body to the lower body. It aids in various functions such as:
Psoas Syndrome is a relatively rare and often misdiagnosed condition that occurs when the psoas muscle – a large muscle located in the lumbar region of the spine that extends through the pelvis – is injured or strained. The psoas muscle is crucial for human movement and stability, connecting the upper body to the lower body. It aids in various functions such as:
- lifting the knees
- bending at the waist
- moving the legs forward during walking
When this muscle is inflamed or irritated, it can cause a range of symptoms. And leading to what is known as Psoas Syndrome. This Syndrome can manifest itself through a series of symptoms. And, these symptoms can be misleading and are often mistaken for other common ailments such as a herniated disc, sciatica, or arthritis due to their similarity. It is this ambiguity, along with a general lack of knowledge about the syndrome, that frequently results in misdiagnosis.
What Are The Symptoms Of Psoas Syndrome?
Psoas Syndrome can present with a variety of symptoms. That can sometimes overlap with other conditions, making diagnosis challenging. Here are some of the common signs and symptoms associated with Psoas Syndrome:
This is often one of the most common symptoms. It may present as a deep, aching pain that can be felt on one or both sides of the lower back.
- Hip Pain
Discomfort can also radiate to the hip region, or the pain may be primarily centered in the hip.
- Pain in the Groin or Thigh
Pain may be felt in the front of the thigh, the groin, or even radiating down the leg. This can be mistaken for a hip flexor strain or a hernia.
- Limited Range of Motion
Individuals with Psoas Syndrome might experience difficulty moving the hip joint. Particularly during certain activities like walking, bending, or lifting the knees.
- Postural Changes
Due to the discomfort, people with Psoas Syndrome may develop an altered gait or posture. Such as a forward-leaning position when standing or walking.
- Abdominal Discomfort
Some people may experience tenderness or discomfort in the lower abdomen due to the location of the psoas muscle.
Remember, these symptoms can be similar to other conditions. So if you’re experiencing them, it’s crucial to seek a medical professional’s advice for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
How Is Psoas Syndrome Diagnosed?
 Diagnosing Psoas Syndrome can be a complex process due to the similarity of its symptoms with other conditions affecting the lower back and hip. Here are the typical steps involved:
Diagnosing Psoas Syndrome can be a complex process due to the similarity of its symptoms with other conditions affecting the lower back and hip. Here are the typical steps involved:
- Patient History
A thorough history of the patient is taken, including a review of the onset of symptoms, activities leading to pain, lifestyle habits, and any past injuries or surgeries.
- Physical Examination
The medical professional will conduct a physical examination. That includes assessing the patient’s posture, range of motion, and the presence of pain when the psoas muscle is stretched or contracted. This often involves specific maneuvers such as the Thomas Test, which can indicate a tight psoas muscle.
- Imaging Tests
While there’s no definitive imaging test for Psoas Syndrome, various techniques can help rule out other conditions and indirectly suggest the presence of Psoas Syndrome. These can include X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans. For example, an MRI might show inflammation around the psoas muscle.
- Diagnostic Injections
In some cases, a diagnostic injection of a local anesthetic into the psoas muscle may be performed. If the pain subsides following the injection, this can confirm the diagnosis of Psoas Syndrome.
- Evaluation by a Specialist
In complex or unclear cases, referral to a specialist. Such as a rheumatologist or orthopedic surgeon, may be necessary for further evaluation.
Because of the complexities involved, it’s essential that individuals experiencing symptoms seek help from healthcare professionals skilled in musculoskeletal disorders to get an accurate diagnosis. It’s also important to remember that treatment should be individualized based on the patient’s unique needs and circumstances.
How Is Psoas Syndrome Different?
Psoas Syndrome is different from many other lower back and hip conditions due to several unique factors:
- Origin of Pain: The pain in Psoas Syndrome originates from the psoas muscle, a deep muscle that is not directly accessible for palpation. This is different from many other causes of back pain, such as disc herniation or facet joint osteoarthritis, where the structures involved are closer to the surface or more readily identified in imaging studies.
- Specific Symptoms: This Syndrome can cause a distinct pattern of symptoms including lower back pain, hip pain, deep abdominal discomfort, and difficulties with certain movements like standing up straight from a seated position, bending at the waist, or lifting the knee.
- Involvement in Various Movements: The psoas muscle plays a key role in many daily movements and activities, from walking and running to sitting and standing. This means that an issue with the psoas muscle, like Psoas Syndrome, can interfere with many aspects of daily life.
- Postural Implications: Since the psoas muscle is crucial for maintaining proper posture, this Syndrome often results in noticeable changes in the individual’s posture or gait, such as a forward-leaning position.
How Do You Fix Psoas Syndrome?
 Treating Psoas Syndrome requires a combination of approaches, including therapeutic interventions, lifestyle changes, and in some cases, medical treatments. Here are some methods used:
Treating Psoas Syndrome requires a combination of approaches, including therapeutic interventions, lifestyle changes, and in some cases, medical treatments. Here are some methods used:
Physical Therapy
This is often the first-line treatment for Psoas Syndrome. A physical therapist can provide targeted exercises to stretch and strengthen the psoas muscle, improve posture, and restore normal movement. Techniques like massage and heat therapy might also be used to relax the muscle and reduce inflammation.
Stretching and Strengthening Exercises
Regular exercises specifically designed to stretch the psoas muscle and strengthen surrounding muscles can significantly improve symptoms and prevent recurrence. These exercises should be done under the guidance of a healthcare professional or a trained physiotherapist to avoid further injury.
Lifestyle Changes
Since prolonged sitting or standing can aggravate Psoas Syndrome, making certain lifestyle changes can help. This may involve taking regular breaks from sitting, improving workstation ergonomics, and maintaining a healthy weight.
Pain Management
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may be used to manage pain and inflammation. Other options include applying heat or cold packs to the affected area, using over-the-counter pain relievers, and in some cases, receiving trigger point injections to numb the psoas muscle.
Surgical Intervention
In severe or persistent cases that do not respond to conservative treatment, surgical intervention may be considered. The goal of surgery is typically to release the psoas tendon, thereby relieving tension and reducing pain.
Mind-Body Techniques
Techniques such as mindfulness, yoga, and Pilates can help manage pain, improve muscle flexibility, and reduce stress.
Remember, these treatments should be undertaken under the supervision of a healthcare provider to ensure they are safe and effective for the individual’s specific situation. It’s crucial to seek professional help if you suspect you have this condition.
What Position Relaxes The Psoas?
To relax the psoas muscle, you can try the “Constructive Rest Position” or “90/90 position”. Here’s how to do it:
Constructive Rest Position
- Lie down on your back on a comfortable, flat surface.
- Bend your knees and plant your feet flat on the floor, hip-width apart. The heels should be a comfortable distance from the buttocks, typically around 16-20 inches.
- Let your arms rest by your sides, palms up or down, whichever feels more comfortable.
- Allow your lower back to adopt a neutral, comfortable curve, not forced into the floor.
- Stay in this position for 10 to 20 minutes, focusing on deep, relaxed breathing.
90/90 position

- Lie on your back on a flat surface.
- Lift your legs so that your hips and knees are bent at a 90-degree angle as if you were sitting in a chair.
- Support your legs with a chair or a wall so that you can relax your hips and lower back.
- Relax your upper body, letting your arms rest by your sides.
- Stay in this position for 5 to 15 minutes, focusing on relaxed breathing.
These positions help to release tension in the psoas muscle by placing the hip joint in a position that encourages the muscle to relax. However, individuals with specific health conditions or injuries should check with their healthcare provider before trying these or any new exercises.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding and managing Psoas Syndrome is an essential component of maintaining overall musculoskeletal health, given the significant role the Psoas muscle plays in our daily activities. While Psoas Syndrome can present various challenges, it is treatable and manageable with the correct approach.
Remember, the key to effective treatment is early recognition and appropriate intervention. Therefore, it’s crucial to seek professional medical advice if you’re experiencing symptoms consistent with Psoas Syndrome. Here’s to a pain-free, active, and healthy life!
If you’re experiencing Back pain, physical therapy for back pain at PhysioMantra can help: Book an online physical therapy session.



