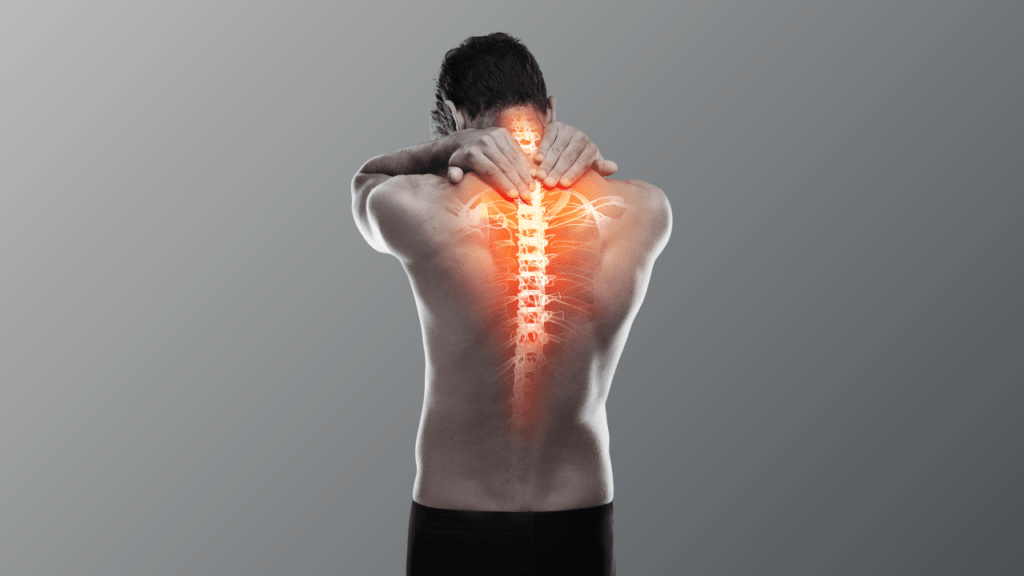
Backbone pain, also known as back pain or spinal pain, is a prevalent health issue that affects millions of people worldwide. It can range from mild discomfort to debilitating pain, significantly impacting a person’s daily life and overall well-being. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and various treatment options for backbone pain. Whether you’re experiencing occasional back discomfort or chronic pain, understanding the available treatments can lead to effective pain management and improved quality of life.
Contents
- 1 Understanding Back Bone Pain
- 2 Causes of Back Bone Pain
- 3 Symptoms and Signs
- 4 Diagnosis and Medical Evaluation
- 5 Non-Surgical Treatments for Back Bone Pain
- 6 Lifestyle Changes and Home Remedies
- 7 Surgical Interventions
- 8 Alternative and Complementary Treatments
- 9 Prevention of Back Bone Pain
- 10 When to Seek Professional Help
- 11 Conclusion
Understanding Back Bone Pain

“Backbone pain” is not a medical term commonly used to describe a specific condition. You may be referring to pain in the back, which is a more general term used to describe discomfort or pain in the area of the spine.
The spine, also known as the backbone, is made up of a series of bones called vertebrae, which protect the spinal cord and provide structural support for the body. Back pain can result from various causes, including muscle strains, ligament sprains, herniated discs, spinal stenosis, osteoarthritis, and other degenerative conditions.
The location and severity of back pain can vary depending on the underlying cause.
Causes of Back Bone Pain
Back pain can have various causes, ranging from mild and temporary issues to more severe and chronic conditions. Some common causes of back pain include:
- Muscle Strain: Overstretching or tearing of muscles or ligaments in the back due to improper lifting, sudden movements, or poor posture.
- Disc Problems: Herniated or bulging discs in the spine can put pressure on nerves, leading to pain. Degenerative disc disease can also cause back pain over time.
- Spinal Stenosis: Narrowing of the spinal canal, which can compress the spinal cord and nerves, causing pain and numbness.
- Osteoarthritis: Degeneration of the joints and discs in the spine due to aging, leading to pain and stiffness.
- Osteoporosis: A condition characterized by weakened bones, which can make the spine more susceptible to fractures and pain.
- Sciatica: Compression or irritation of the sciatic nerve, which runs from the lower back down through the legs, causing sharp pain, tingling, or numbness.
Symptoms and Signs
The symptoms and signs of back pain can vary depending on the underlying cause and the affected area of the spine. Some common symptoms and signs of back pain include:
- Pain: The primary and most common symptom is pain in the back. The pain may be dull, aching, sharp, or stabbing, and it can range from mild to severe.
- Stiffness: Back pain can often be accompanied by stiffness, making it difficult to move or bend the back.
- Limited Range of Motion: You may find it challenging to perform certain movements due to pain and stiffness.
- Muscle Spasms: In some cases, the muscles in the back may go into spasms, causing sudden and intense pain.
- Radiating Pain: If the pain is due to nerve compression or irritation, it may radiate down the leg (sciatica) or to other areas of the body.
- Numbness and Tingling: Compression of nerves can lead to sensations of numbness, tingling, or “pins and needles” in the back, legs, or arms.
Diagnosis and Medical Evaluation
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for determining the appropriate treatment plan. A medical evaluation may include:
- Physical Examination: Assessing the spine’s flexibility, and range of motion, and identifying areas of tenderness.
- Imaging Tests: X-rays, MRI, or CT scans may be used to visualize the spine’s structure and identify any abnormalities.
- Laboratory Tests: Blood tests can help rule out certain medical conditions that may contribute to back pain.
Non-Surgical Treatments for Back Bone Pain

Non-surgical treatments for back pain aim to alleviate pain, reduce inflammation, improve mobility, and promote healing. The choice of treatment will depend on the underlying cause of the back pain. Here are some common non-surgical treatments for back pain:
- Rest: Giving your back time to rest can help reduce inflammation and relieve strain on the affected area. However, extended bed rest is generally not recommended, as it may lead to muscle weakness and stiffness. Short periods of rest combined with gentle movement are often more beneficial.
- Physical Therapy: A physical therapist can create a personalized exercise program to strengthen the back and core muscles, improve flexibility, and promote proper posture. Physical therapy may also include modalities like heat or ice therapy, ultrasound, or electrical stimulation.
- Pain Medication: Over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen or naproxen, can help reduce pain and inflammation. If the pain is severe, a doctor may prescribe stronger medications for short-term use.
- Heat and Cold Therapy: Applying heat packs or taking warm baths can help relax tense muscles and improve blood flow to the area. Cold packs can reduce inflammation and numb the area to ease the pain.
Lifestyle Changes and Home Remedies
Lifestyle changes and home remedies can complement medical treatments and help manage back pain effectively. Here are some lifestyle changes and home remedies that may provide relief from back pain:
- Exercise: Engaging in regular, low-impact exercises can help strengthen the back muscles, improve flexibility, and support the spine. Activities like walking, swimming, and cycling can be beneficial. However, avoid high-impact exercises or activities that may worsen the pain.
- Maintain Good Posture: Practice good posture while sitting, standing, and lifting to reduce strain on your back. Use ergonomic chairs and ensure your workstations are set up correctly.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce stress on the spine and lower the risk of back pain. Adopt a balanced diet and engage in regular physical activity to manage weight.
- Proper Lifting Technique: When lifting objects, bend your knees and keep the object close to your body. Avoid twisting while lifting and use your legs and core muscles to lift, rather than straining your back.
- Stay Active: Avoid prolonged periods of inactivity or sitting. Take breaks to stretch and move around throughout the day, especially if you have a sedentary job.
Surgical Interventions

Here are some common surgical interventions for back pain:
- Discectomy: This procedure involves removing part or all of a herniated or damaged intervertebral disc that may be compressing a nerve and causing pain.
- Laminectomy: In a laminectomy, a part of the lamina (a bony structure in the spine) is removed to create more space for the spinal cord and nerves, relieving pressure and pain.
- Spinal Fusion: Spinal fusion is a procedure that involves permanently joining two or more vertebrae together to stabilize the spine and reduce pain caused by conditions like spinal instability, degenerative disc disease, or spondylolisthesis.
- Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty: These procedures are used to treat vertebral compression fractures caused by osteoporosis or other conditions. They involve injecting cement-like materials into the fractured vertebra to provide support and relieve pain.
- Artificial Disc Replacement: In this surgery, a damaged intervertebral disc is replaced with an artificial disc to maintain motion and stability in the spine.
Alternative and Complementary Treatments
Some individuals find relief from backbone pain through alternative therapies, such as:
- Massage Therapy: Manipulation of muscles can promote relaxation and reduce pain.
- Yoga and Pilates: These exercises improve flexibility and core strength.
- Herbal Supplements: Certain herbs may have anti-inflammatory properties that alleviate pain.
Prevention of Back Bone Pain
Here are some tips for preventing back pain:
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess weight can put strain on the spine and lead to back pain. Maintain a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise.
- Exercise Regularly: Engage in regular physical activity to strengthen your back and core muscles. Low-impact exercises like walking, swimming, and yoga are particularly beneficial.
- Practice Good Posture: Be mindful of your posture while sitting, standing, and lifting. Avoid slouching and use ergonomic furniture to support your back.
- Use Proper Lifting Techniques: When lifting heavy objects, bend your knees and keep the object close to your body. Avoid twisting while lifting.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking can impair blood flow to the spine and hinder healing. Quitting smoking can improve overall health and reduce the risk of back pain.
When to Seek Professional Help
You should seek professional help for back pain in the following situations:
- Severe Pain: If you experience severe and persistent back pain that does not improve with rest or over-the-counter pain medication, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional.
- New or Worsening Pain: If you develop new or worsening back pain, especially after an injury or accident, it’s crucial to get medical attention to rule out serious underlying causes.
- Pain with Numbness or Weakness: If you have back pain accompanied by numbness, tingling, or weakness in the legs or arms, it may indicate nerve compression, and immediate medical evaluation is necessary.
- Loss of Bowel or Bladder Control: If you experience loss of bowel or bladder control along with back pain, it could be a sign of a serious condition called cauda equina syndrome, which requires immediate medical attention.
Conclusion
Backbone pain can significantly impact a person’s life, but with the right approach to diagnosis and treatment, relief is possible. From lifestyle changes and non-surgical treatments to alternative therapies and surgical interventions, a range of options exists. By adopting preventive measures and seeking timely medical attention, individuals can take control of their backbone pain and enjoy improved mobility and overall well-being.
If you’re experiencing Back pain, physical therapy for back pain at PhysioMantra can help: Book an online physical therapy session.