Gluteal tendinopathy is a common yet often overlooked source of pain in the hip region. This condition occurs when the tendons that connect the gluteal muscles to the hip bone become inflamed. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the anatomy of gluteal tendinopathy, discover what triggers this condition, explore how it’s diagnosed, and offer guidance on effective treatment strategies.
Contents
What Is Gluteal Tendinopathy?
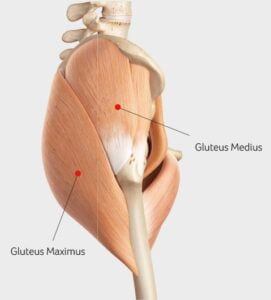 Gluteal tendinopathy is a painful and debilitating condition that affects the tendons of the gluteal muscles. It specifically the gluteus medius and gluteus minimus tendons, located around the hip region. It is characterized by inflammation and degeneration of these tendons. And leading to localized pain and tenderness. This condition is often caused by repetitive or excessive use of the hip muscles or many others.
Gluteal tendinopathy is a painful and debilitating condition that affects the tendons of the gluteal muscles. It specifically the gluteus medius and gluteus minimus tendons, located around the hip region. It is characterized by inflammation and degeneration of these tendons. And leading to localized pain and tenderness. This condition is often caused by repetitive or excessive use of the hip muscles or many others.
This condition typically manifests as pain on the outer side of the hip. That may radiate down the outer thigh or buttocks. The discomfort is usually worse during activities that involve weight-bearing on the affected leg and can severely impact daily activities. Early diagnosis and appropriate management are essential to alleviate symptoms and improve function for those suffering from gluteal tendinopathy.
Is It OK To Walk With Gluteal Tendinopathy?
Walking with gluteal tendinopathy can be possible. But it may cause discomfort and pain, especially during weight-bearing on the affected leg. The level of pain experienced while walking can vary depending on the severity of the condition and individual tolerance to discomfort. In some cases, walking may exacerbate the symptoms and lead to increased inflammation in the gluteal tendons.
However, completely avoiding walking is not advisable. As it may result in muscle weakness and joint stiffness, which can further worsen the condition. Instead, a balanced approach is recommended. Here are some suggestions to manage walking with gluteal tendinopathy:
- Reduce Intensity and Duration: If walking is causing significant pain, consider reducing the distance or duration of your walks. Gradually increase the time spent walking as your symptoms improve.
- Modify Walking Technique: Pay attention to your walking technique and try to maintain a neutral spine and pelvis alignment. Avoid excessive hip rotation or sideways movements that may strain the gluteal tendons.
- Use Assistive Devices: If needed, consider using assistive devices like a cane or walking stick on the opposite side to reduce the load on the affected hip.
Remember, everyone’s condition is unique. And it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice on managing gluteal tendinopathy and safely incorporating walking into your routine.
What Does Gluteal Tendinopathy Feel Like?
 Gluteal tendinopathy typically causes pain and discomfort in the hip region. The pain is commonly felt on the outer side of the hip, just below the bony prominence called the greater trochanter. The sensation of pain can vary from mild to severe and may be described as:
Gluteal tendinopathy typically causes pain and discomfort in the hip region. The pain is commonly felt on the outer side of the hip, just below the bony prominence called the greater trochanter. The sensation of pain can vary from mild to severe and may be described as:
- Tenderness: The affected area may feel tender to touch or pressure, particularly over the gluteal tendons.
- Sharp or Stabbing Pain: The pain can be sharp or stabbing, especially during activities that involve weight-bearing on the affected hip. Such as walking, running, or climbing stairs.
- Aching or Throbbing: Some individuals may experience a dull, aching pain or throbbing sensation in the hip region, even during rest.
- Pain with Movement: Certain movements of the hip, such as lifting the leg out to the side or rotating it, may exacerbate the pain.
- Pain at Night: Some people may report increased pain at night, especially when lying on the affected side.
- Reduced Mobility: Gluteal tendinopathy can lead to a reduced range of motion in the hip joint. And difficulty performing certain activities that involve hip movements.
It’s important to note that the symptoms of gluteal tendinopathy can vary from person to person. Additionally, other conditions, such as hip osteoarthritis or bursitis, can produce similar symptoms. So an accurate diagnosis by a healthcare professional is crucial for effective management.
What Are The Potential Causes Of It?
The development of gluteal tendinopathy can be attributed to various potential causes. Some of the common factors that contribute to this condition include:
- Overuse or Repetitive Movements
Engaging in activities that involve repetitive movements of the hip, such as running, jumping, or climbing stairs. All this can place excessive strain on the gluteal tendons, leading to inflammation and degeneration.
- Hip Muscle Weakness
Weakness in the gluteal muscles, especially the gluteus medius, and minimus, can place additional stress on the tendons. As they try to compensate for the lack of muscle support, increasing the risk of tendinopathy.
- Sudden or Excessive Trauma
A direct injury or trauma to the hip region, such as a fall or impact, can damage the gluteal tendons and trigger tendinopathy.
- Age and Degeneration
As individuals age, tendons naturally undergo degenerative changes. Eventually, making them more susceptible to injuries and inflammation.
- Biomechanical Factors
Abnormalities in the hip or lower limb biomechanics, such as altered gait patterns or imbalances. And this can place uneven stress on the gluteal tendons, contributing to their degeneration.
- Occupational Factors
Certain occupations that require prolonged periods of standing, walking, or heavy lifting may increase the risk of gluteal tendinopathy due to the repetitive nature of the tasks.
- Muscle Imbalance
Imbalances in the muscles around the hip, such as tightness in the hip flexors or weakness in the glutes. And it can impact the distribution of forces during movement. That potentially leads to tendinopathy.
It is crucial to identify and address the underlying causes of gluteal tendinopathy to effectively manage the condition and prevent it from recurring.
What Is The Best Treatment For Gluteal Tendinopathy?
 The best treatment typically involves a combination of conservative approaches and addressing the underlying factors contributing to the condition. While the treatment may vary based on individual circumstances, here are some common approaches:
The best treatment typically involves a combination of conservative approaches and addressing the underlying factors contributing to the condition. While the treatment may vary based on individual circumstances, here are some common approaches:
Rest and Activity Modification
Give the affected hip time to rest and avoid activities that exacerbate pain or strain the gluteal tendons. Modify daily activities and exercises to reduce the load on the hip while it heals.
Physical Therapy
A structured physical therapy program is essential for gluteal tendinopathy. It focuses on strengthening the gluteal muscles, improving hip stability, and correcting any biomechanical imbalances. Therapists may use techniques like eccentric exercises, stretching, and manual therapy to aid recovery.
Pain Management
Over-the-counter pain medications or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help manage pain and reduce inflammation. However, it’s essential to use them under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Ice and Heat Therapy
Applying ice packs to the affected area can help reduce inflammation and alleviate pain. Heat therapy can also be beneficial in improving blood flow and promoting healing.
Corticosteroid Injections
In some cases, a healthcare professional may administer corticosteroid injections into the affected area to provide short-term pain relief and reduce inflammation. However, these injections are not recommended for long-term use due to potential side effects and the risk of tendon degeneration.
Weight Management
If the individual is overweight or obese, losing excess weight can significantly reduce the load on the hip and improve symptoms.
Education and Self-Management
Learning about gluteal tendinopathy, its causes, and appropriate self-management strategies is crucial for long-term recovery. This may include learning proper warm-up techniques, exercises to avoid, and lifestyle adjustments.
It’s important to note that the success of treatment may vary from person to person. Some individuals may experience significant improvement with conservative measures alone. While others may require more advanced interventions if conservative methods do not provide sufficient relief. If you suspect you have gluteal tendinopathy or are experiencing hip pain, it’s essential to seek guidance from a healthcare professional.
Conclusion
In conclusion, gluteal tendinopathy is a challenging and often underestimated condition affecting the tendons of the gluteal muscles, causing pain and discomfort in the hip region. From its potential causes, including overuse, biomechanical factors, and age-related degeneration, to the various treatment options available. While walking with gluteal tendinopathy may be possible, it’s essential to strike a balance between rest and gradual activity to avoid exacerbating the symptoms.
By seeking professional guidance, implementing targeted exercises, and making necessary lifestyle adjustments, individuals can take control of their hip health and regain mobility. If you’re experiencing Hip pain, physical therapy for hip pain at PhysioMantra can help: Book an online physical therapy session.