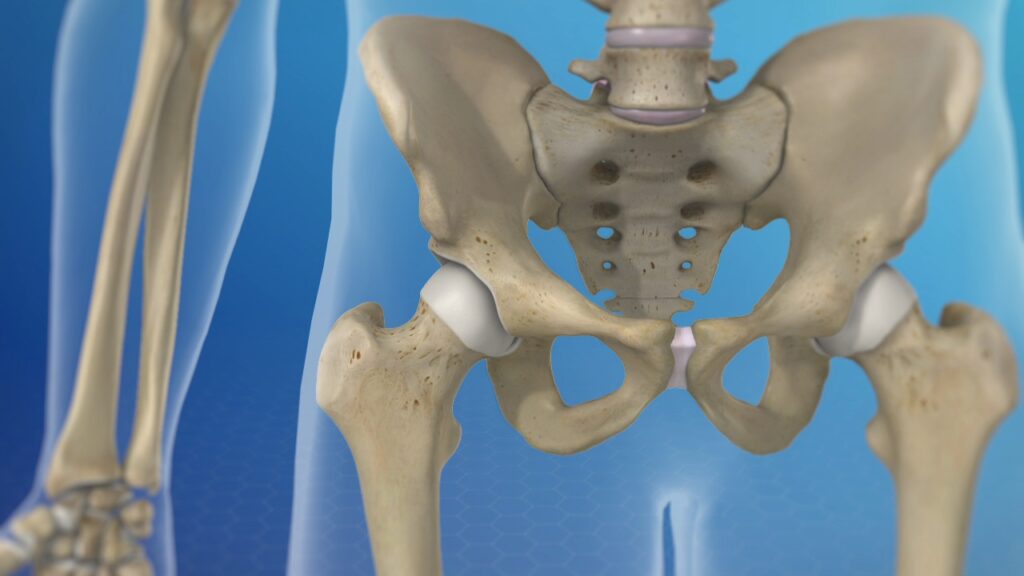
The hip joint is a vital part of our body, responsible for supporting our weight, enabling movement, and maintaining stability. It is a ball and socket joint, where the rounded head of the femur (thigh bone) fits into the cup-shaped acetabulum of the pelvis. While this joint is designed to withstand significant stresses, it can still be susceptible to various problems that can cause discomfort and limit mobility. In this blog, we will delve into the common hip ball and socket joint problems, their causes, symptoms, and potential treatment options.
Contents
- 1 Anatomy of the Hip Ball and Socket Joint
- 2 Common Problems with the Hip Joint
- 3 Causes of Hip Ball and Socket Joint Problems
- 4 Signs and Symptoms of Hip Joint Issues
- 5 Diagnosis of Hip Joint Problems
- 6 Conservative Treatments for Hip Joint Issues
- 7 Surgical Interventions for Hip Joint Problems
- 8 Rehabilitation and Recovery
- 9 Preventing Hip Joint Problems
- 10 Tips for Managing Hip Joint Pain
- 11 Hip Joint Health for Athletes
- 12 Alternative Therapies for Hip Joint Pain
- 13 Living with Hip Joint Issues
- 14 Conclusion
Anatomy of the Hip Ball and Socket Joint
The hip joint is a complex and vital joint in the human body that allows for a wide range of movements, including walking, running, and jumping. It is a ball and socket joint, also known as a “spheroidal joint,” due to its unique structure, which provides stability and mobility. Let’s explore the anatomy of the hip ball and socket joint:
1. Bones: The hip joint involves the articulation between two main bones:
- Femur (Thigh Bone): The femur is the longest bone in the human body and forms the “ball” component of the ball and socket joint. Its rounded head (femoral head) articulates with the socket of the pelvis.
- Pelvis (Acetabulum): The pelvis is a large, bony structure that consists of three bones: ilium, ischium, and pubis. The cup-shaped cavity, known as the acetabulum, is formed where these three bones meet. The acetabulum houses the femoral head to create the “socket” part of the joint.
2. Articular Cartilage: Both the femoral head and the acetabulum are covered with a layer of smooth, slippery cartilage known as articular cartilage. This cartilage helps reduce friction between the bones during movement and allows for smooth gliding motion within the joint.
Common Problems with the Hip Joint

Several issues can affect the hip ball and socket joint, with some of the most common ones being:
1. Osteoarthritis of the Hip: Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease that occurs when the protective cartilage on the ends of bones wears down over time, leading to friction, inflammation, and pain.
2. Hip Bursitis: Bursae are small fluid-filled sacs that cushion the bones, tendons, and muscles near the joints. Inflammation of the bursae can cause hip pain and limited movement.
3. Hip Labral Tears: The labrum is a ring of cartilage that lines the outer rim of the acetabulum. Tears in the labrum can result from injury or structural abnormalities, causing pain and instability.
4. Hip Impingement: Also known as femoroacetabular impingement (FAI), this condition occurs when there is abnormal contact between the femoral head and the acetabulum, leading to damage and pain.
Causes of Hip Ball and Socket Joint Problems
Several factors can contribute to the development of hip joint issues, including:
1. Aging and Wear and Tear: As we age, the cartilage in the hip joint may naturally deteriorate, increasing the risk of conditions like osteoarthritis.
2. Injuries and Trauma: Sports injuries, falls, or accidents can damage the hip joint, leading to long-term problems.
3. Genetic Factors: Some individuals may be predisposed to hip joint issues due to their genetic makeup.
4. Overuse and Repetitive Motion: Engaging in activities that place excessive strain on the hip joint over time can contribute to joint problems.
Signs and Symptoms of Hip Joint Issues
Recognizing the signs of hip joint problems is essential for timely diagnosis and treatment. Common symptoms include:
1. Pain and Discomfort in the Hip Area: Persistent pain in the hip joint or groin area, especially during movement or weight-bearing activities.
2. Reduced Range of Motion: Difficulty in performing activities that require bending or rotating the hip joint.
3. Stiffness and Swelling: The hip joint may feel stiff and inflamed, especially after periods of rest or inactivity.
4. Clicking or Popping Sensations: Some individuals may experience clicking or popping sounds when moving the hip joint.
Diagnosis of Hip Joint Problems

Here’s an overview of the diagnostic process for hip joint problems:
Imaging Studies: Imaging tests are crucial for visualizing the structures within the hip joint and identifying abnormalities. Common imaging modalities used in the diagnosis of hip joint problems include:
- X-rays: X-rays provide detailed images of bones and can help identify conditions like osteoarthritis, fractures, or structural abnormalities in the hip joint.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): MRI uses powerful magnets and radio waves to produce detailed images of soft tissues like cartilage, ligaments, and muscles. It is helpful in diagnosing conditions like labral tears, hip impingement, and avascular necrosis.
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scan: CT scans provide detailed cross-sectional images of bones and can be useful for evaluating complex fractures or bone abnormalities.
- Ultrasound: Ultrasound is used to visualize soft tissues and can help assess hip bursitis or identify fluid accumulation within the joint.
4. Laboratory Tests: In certain cases, laboratory tests may be ordered to rule out or confirm specific medical conditions associated with hip joint problems. Blood tests can help identify inflammatory markers, infection, or underlying systemic diseases like rheumatoid arthritis.
Conservative Treatments for Hip Joint Issues
In the early stages or mild cases, conservative treatments may be effective in managing hip joint problems. These include:
1. Rest and Activity Modification: Giving the hip joint adequate rest and avoiding activities that exacerbate the pain.
2. Physical Therapy and Exercises: Strengthening exercises and physical therapy can improve joint stability and flexibility.
3. Pain-Relief Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers or prescribed medications can help manage pain and inflammation.
4. Assistive Devices: The use of canes or other walking aids can reduce the pressure on the hip joint during movement.
Surgical Interventions for Hip Joint Problems
For more severe cases or when conservative treatments do not provide relief, surgery may be necessary. Some common surgical interventions include:
1. Hip Replacement Surgery: In this procedure, the damaged hip joint is replaced with an artificial joint made of metal or ceramic materials.
2. Hip Resurfacing: This surgery involves reshaping the damaged hip joint while preserving more bone than traditional hip replacement.
3. Hip Arthroscopy: A minimally invasive procedure that allows the surgeon to repair or remove damaged tissues through small incisions.
4. Minimally Invasive Procedures: Advanced techniques that require smaller incisions and reduce recovery time.
Rehabilitation and Recovery
Following any hip surgery, rehabilitation is vital to ensure a successful recovery and restore optimal function. Rehabilitation may involve:
1. Post-Surgery Rehabilitation: Guided exercises and physical therapy to strengthen the hip and surrounding muscles.
2. Physical Therapy Exercises: A tailored exercise program to regain flexibility, strength, and balance.
3. Lifestyle Modifications for Long-Term Recovery: Adopting healthy habits to support the healing process and prevent future issues.
Preventing Hip Joint Problems
While not all hip joint problems can be prevented, some lifestyle choices can help reduce the risk:
1. Maintaining a Healthy Weight: Excess weight can put additional stress on the hip joint, leading to wear and tear.
2. Regular Exercise and Stretching: Engaging in low-impact exercises and stretching can keep the hip joint flexible and strong.
3. Proper Body Mechanics: Using correct body mechanics during daily activities can reduce strain on the hip joint.
4. Avoiding High-Impact Activities: Limiting high-impact activities or using appropriate protective gear can minimize joint stress.
Tips for Managing Hip Joint Pain
If you experience hip joint pain, several strategies can provide relief and improve daily comfort:
1. Using Heat and Cold Therapy: Applying heat or cold packs to the hip area can reduce inflammation and ease pain.
2. Over-the-Counter Pain Medications: Non-prescription pain relievers can help manage mild to moderate hip pain.
3. Joint-Friendly Exercises: Opt for low-impact exercises that are gentle on the hip joint, such as swimming or cycling.
4. Rest and Relaxation Techniques: Taking breaks and practicing relaxation techniques can alleviate joint strain.
Hip Joint Health for Athletes
Athletes and active individuals should consider specific strategies to maintain their hip joint health:
1. Injury Prevention Strategies: Engage in proper warm-ups, cool-downs, and stretching routines to reduce the risk of hip injuries.
2. Cross-Training and Strength Exercises: Incorporate exercises that target hip muscles to improve stability and prevent injuries.
3. Importance of Rest and Recovery: Allow sufficient time for rest and recovery between intense workouts to avoid overuse injuries.
Alternative Therapies for Hip Joint Pain
In addition to conventional treatments, some people find relief from hip joint pain through alternative therapies:
1. Acupuncture and Acupressure: Traditional Chinese therapies that involve stimulating specific points to alleviate pain and promote healing.
2. Chiropractic Care: Manual manipulation of the spine and joints to improve mobility and reduce pain.
3. Herbal Supplements and Remedies: Some natural supplements may help reduce inflammation and support joint health.
4. Mind-Body Practices: Techniques like yoga and meditation can help manage pain and promote relaxation.
Living with Hip Joint Issues
Coping with hip joint problems can be challenging, but several strategies can improve the quality of life:
1. Coping with Chronic Pain: Seeking support from healthcare professionals and loved ones to manage chronic pain effectively.
2. Support Groups and Resources: Joining support groups or seeking online resources can provide valuable information and emotional support.
3. Assistive Devices for Daily Activities: Using aids like handrails or reaching tools can make daily tasks more manageable.
4. Emotional Well-Being and Mental Health: Prioritizing mental well-being and seeking professional help if needed.
Conclusion
Maintaining the health of the hip ball and socket joint is crucial for overall mobility and well-being. If you experience any hip joint issues, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan. By adopting a proactive approach to hip joint health and taking appropriate measures, you can continue to lead an active and fulfilling life.
If you’re experiencing Hip pain, physical therapy for hip pain at PhysioMantra can help: Book an online physical therapy session.